FIGURE 2.
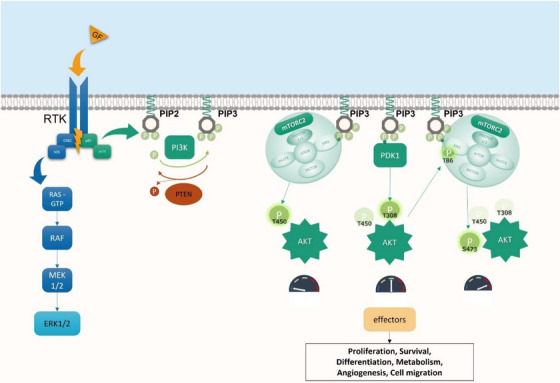
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, MAPK pathway and full AKT activation mechanism. Activation of the PI3K‐AKT‐mTOR pathway (green) is initiated by the activation of various receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) by their ligands. The catalytic subunits of PI3K are then activated upon binding of its regulatory subunits to the pYXXM motifs on RTKs. Once activated, it phosphorylates the membrane phospholipid PtdIns(4,5)P2 (PIP2) to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (PIP3), which functions as a potent second messenger molecule by recruiting to the plasma membrane various kinases such as AKT and PDK1 via their Pleckstrin Homology (PH) domain. Phosphatase and TENsin homolog (PTEN) are a lipid phosphatase that antagonizes the function of PI3K by dephosphorylating PIP3 back to PIP2. Whereas PIP3 directly recruits and activates mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2), AKT is first phosphorylated on his TM (T450) during translation by mTORC2, then on the T‐Loop (T308) by PDK1, increasing its kinase activity. TM and T‐LOOP phosphorylation are responsible of the activation of SIN1 (T86) and finally, mTORC2 is responsible of the last phosphorylation on hydrophobic motif of AKT (S473) for is full activation. MAPK pathway is represented in blue. GF, growth factor.
