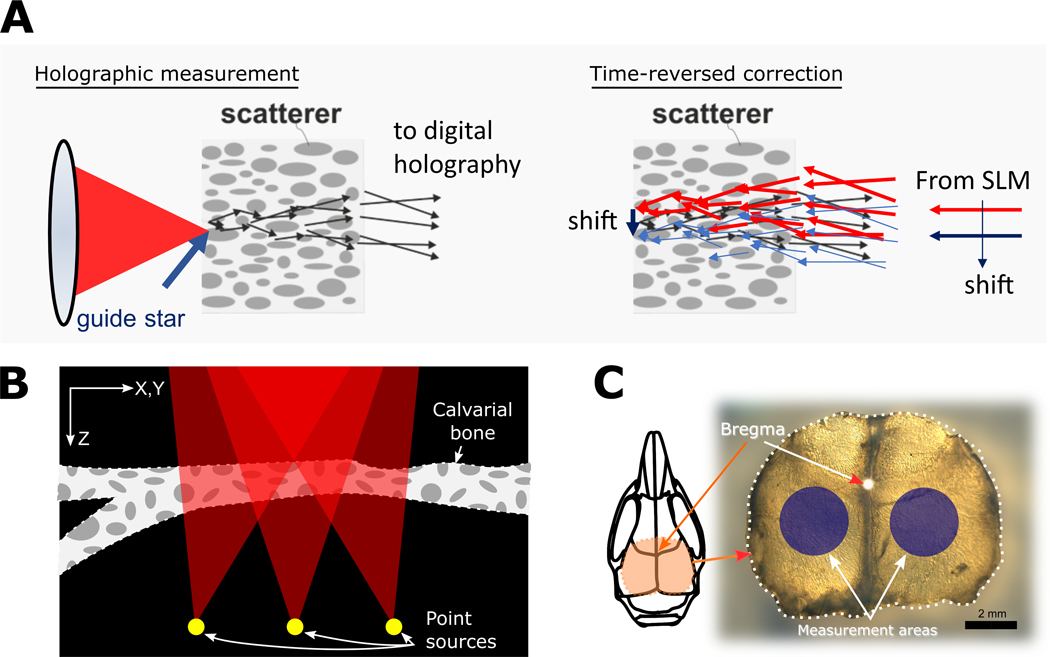
FIGURE 1.
The principle of the DOPC measurement is depicted in (A). A guide star point source is created by focusing on the distal side of the skull (left). The light that transmits through the skull acts as the object beam and interferes on a digital camera with a reference beam, recording a hologram. The phase conjugate information is time-reversed using a spatial light modulator (SLM) to produce a focus at the guide star position. By shifting the correcting phase mask laterally on the SLM, the focus can be shifted; hence IP measurement can be performed. In (B) a presentation of PART method phase accumulation for each point source over a stack of SHG signal is shown. Several point sources are modeled at the bottom of the refractive-index mapped volume, and by ray tracing to the back-pupil-plane the wavefront is reconstructed. Red triangles represent the cone of focus, calculated using the numerical aperture of the objective lens. An extracted skull is shown in (C), with the measurement areas shown in blue circles. These areas are used in many experiments for imaging of cortical layers. Scale bar is 2mm.