Figure 1.
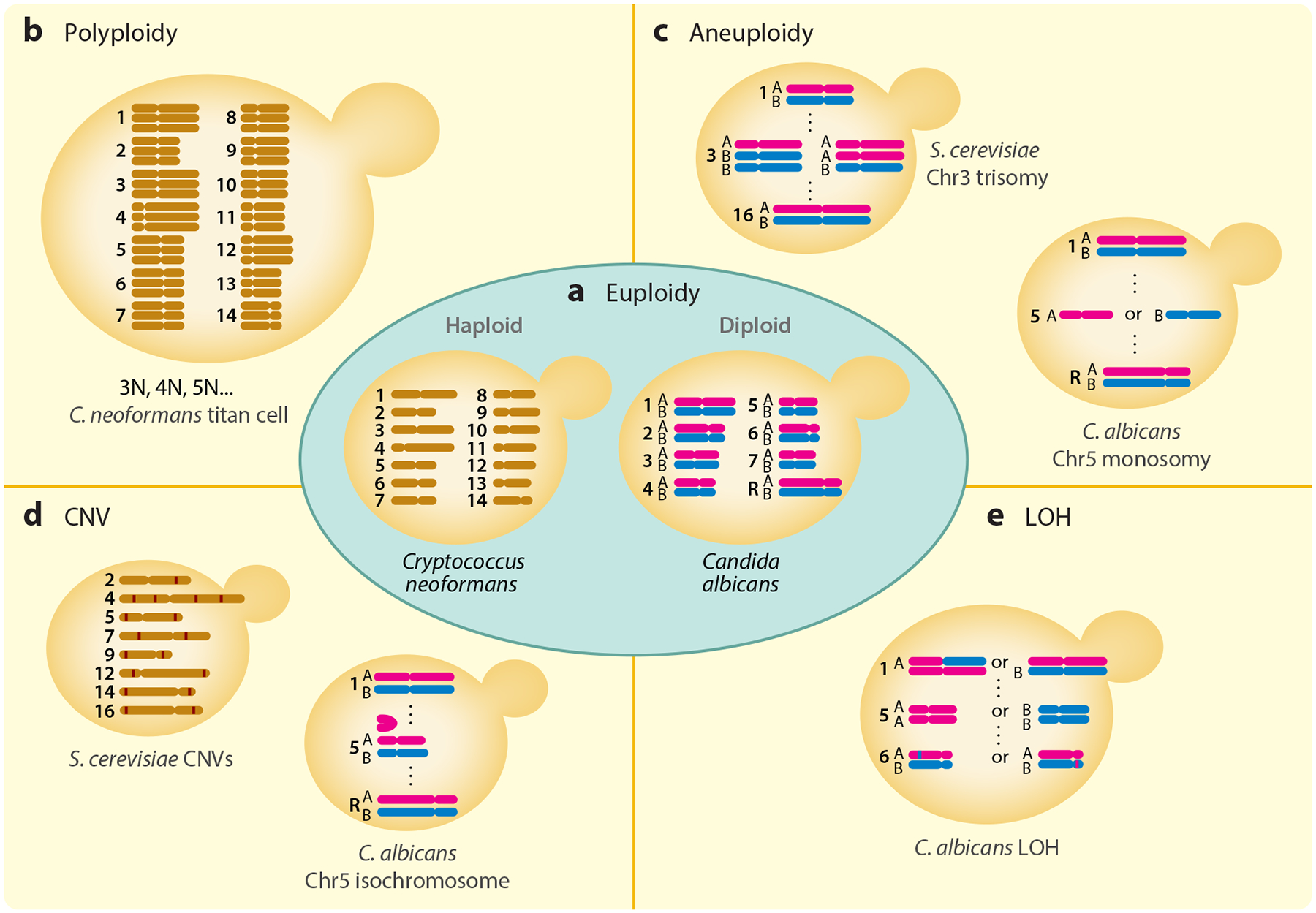
Examples of fungal cells exhibiting genomic changes. (a) Two representative euploid species: haploid (1N) Cryptococcus neoformans and diploid (2N) Candida albicans. (b) An example of polyploidy: C. neoformans titan cells contain at least 3 copies of the entire genome (3N and higher). (c) Examples of aneuploidy: Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome 3 trisomy and C. albicans chromosome 5 monosomy. (d) Example representation of many short intrachromosomal copy number variations (CNVs) in S. cerevisiae (red lines indicate increased copy number of that chromosomal region) and C. albicans isochromosome 5L. (e) An example of loss-of-heterozygosity (LOH) events in C. albicans includes short-tract LOH, long-tract LOH, and whole-chromosome LOH. Figure adapted from images created in BioRender.com.
