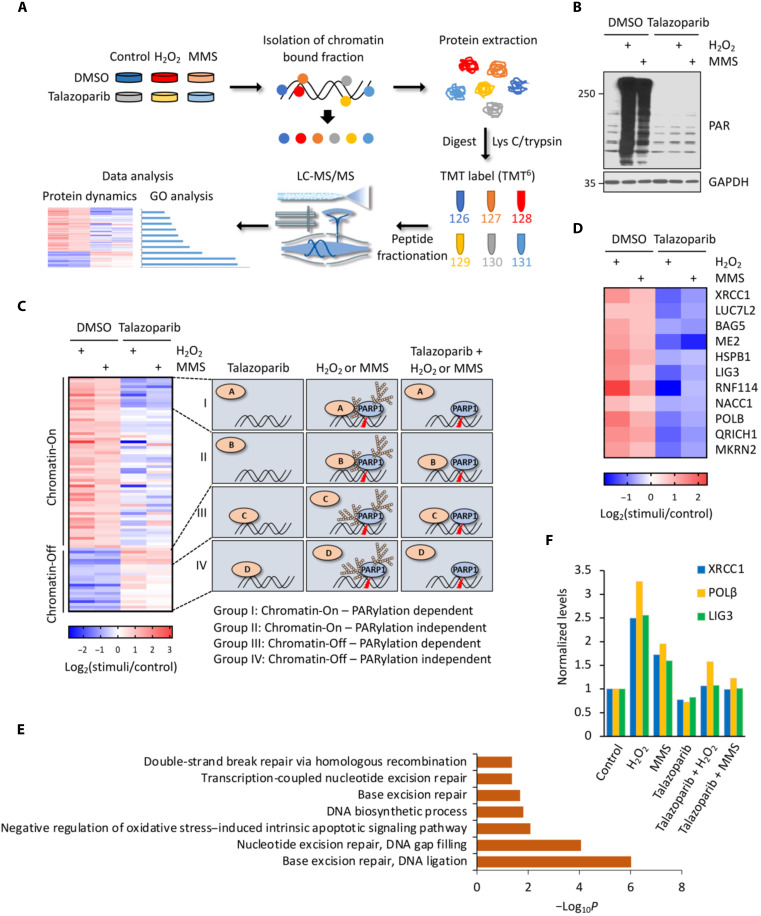
Fig. 1. A chromatin relocalization screen for the identification of PARylation-dependent DNA repair factors.
(A) Overall scheme of the experimental procedures for chromatin relocalization screen. (B) Immunoblot analyses of the whole-cell lysate samples derived from (A). (C) Hierarchical clustering of the relocalized proteins in response to genotoxic stress. The identified proteins were further classified into four categories, i.e., group I (Chromatin-On; PARylation dependent); group II (Chromatin-On; PARylation independent); group III (Chromatin-Off; PARylation dependent); and group IV (Chromatin-Off; PARylation independent). See the main text for the detailed description of these four classes of proteins. (D) A detailed heatmap of all group I proteins. (E) Gene Ontology (GO) analyses of the group I proteins (Chromatin-On; PARylation-dependent proteins) identified from the chromatin relocalization screen. (F) Abundances of representative group I proteins (i.e., XRCC1, POLβ, and LIG3) in the chromatin fraction as determined from the chromatin relocalization screen. LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase;MMS, methyl methanesulfonate; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; TMT, tandem mass tag.