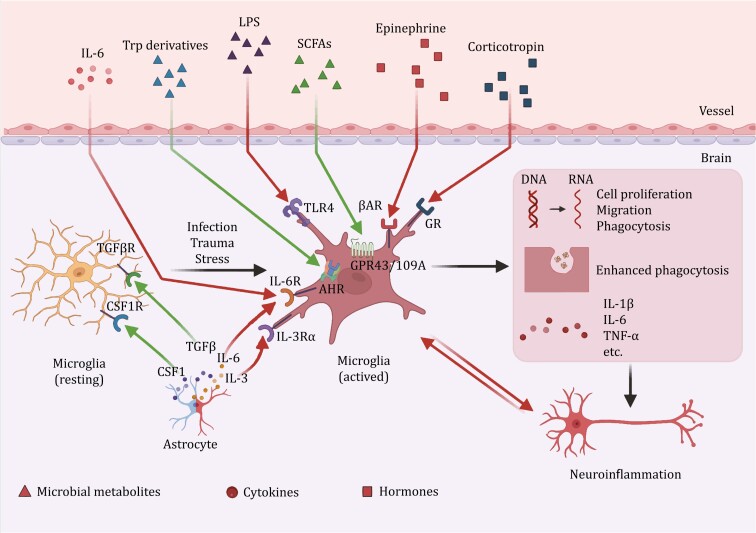
Figure 2.
Homeostasis and activation of microglia. Resting microglia maintain homeostasis under the regulation of cytokines secreted by astrocytes and other cells. However, under conditions such as infection, trauma and stress, microglia are activated by various microbial metabolites, cytokines and hormones, leading to pro-inflammatory manifestations, causing neuroinflammation in the CNS and PNS. SCFAs and tryptophan derivatives play roles in inhibiting microglial activation. The red arrows represent pro-inflammatory pathways, and the green arrows represent mediators that inhibit inflammation or maintain normal growth and development of microglia. AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; βAR, beta adrenergic receptor; CSF1, colony-stimulating factor 1; CSF1R, CSF1 receptor; GPR43/109A, G protein-coupled receptor 43/109A; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; IL, interleukin; IL-3Rα, IL-3 receptor alpha; IL-6R, IL-6 receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; TGFβ: transforming growth factor beta; TGFβR, TGFβ receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; Trp, tryptophan.