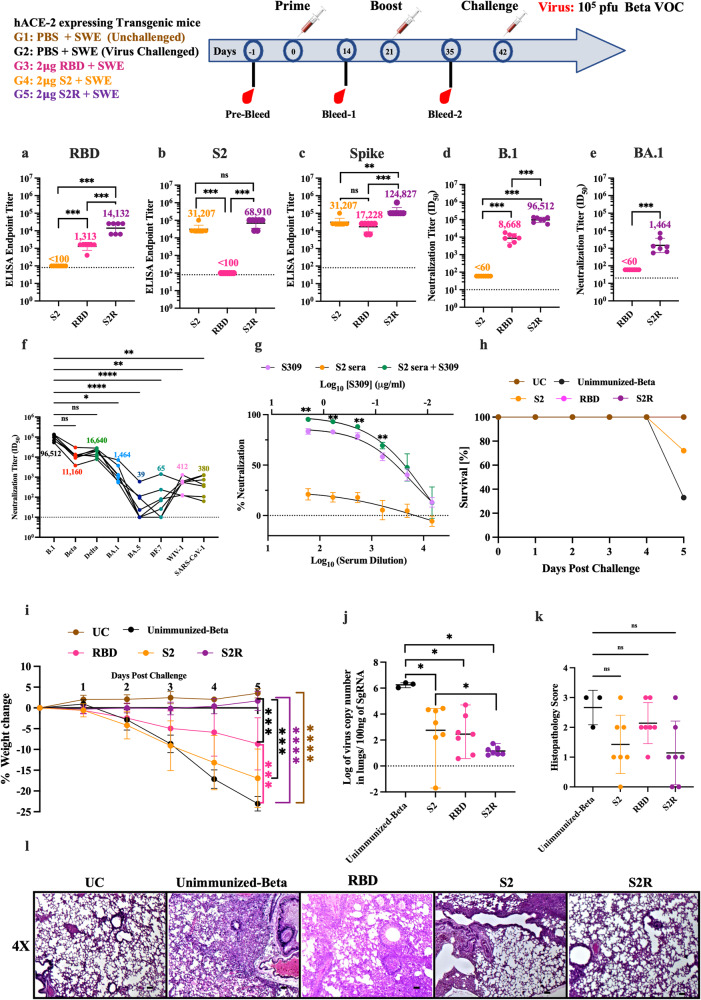
Fig. 3. Immunogenicity of RBD, S2 and S2R in hACE-2 expressing mice.
Three groups of hACE-2 expressing transgenic mice were primed and boosted with 2 μg of RBD, S2 and S2R respectively, followed by an intranasal challenge with 105 pfu of the beta variant of SARS-CoV-2. a–c ELISA endpoint titers against RBD, S2, and spike ectodomain respectively two weeks post-boost. d, e Neutralizing antibody titers elicited by RBD, S2, and S2R against B.1 and BA.1 Omicron SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus. No neutralization was seen with S2 immunized animals. f Neutralizing antibody titers elicited by S2R against various pseudoviruses. Lines connect the neutralizing titers for different variants in a sera sample from an individual animal against different variants. g Neutralization curves of pooled S2 immunized mice sera, monoclonal antibody S309, and S2 immunized mice sera in presence of S309. The sera sample was tested in five technical repeats. Each point represents the median of five independent values. h Survival Curve. i Average weight changes up to 5 days post-challenge. j Lung viral titer. k Histopathology scores of lungs. l Histology of lung tissue sections from unimmunized-unchallenged control (UC), unimmunized- Beta variant challenged control (Unimmunized-Beta) and mice immunized with RBD, S2 and S2R at 4X magnification. The scale bar indicates 50 µm. Titers are shown as geometric mean with geometric SD. The ELISA binding, neutralization titer, lung viral titer and histopathology score data were analyzed with a two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. Neutralizing titers elicited by individual sera in S2R immunized animals against various pseudoviruses (3f) were analyzed with non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple correction. Weight changes (3i) were analyzed with a Multiple Student’s t test with Bonferroni Dunn’s correction method. (ns indicates non-significant, * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, **** indicates p < 0.0001).