Figure 3. Loss of Lmna in OLs does not interfere with the early stages of developmental myelination.
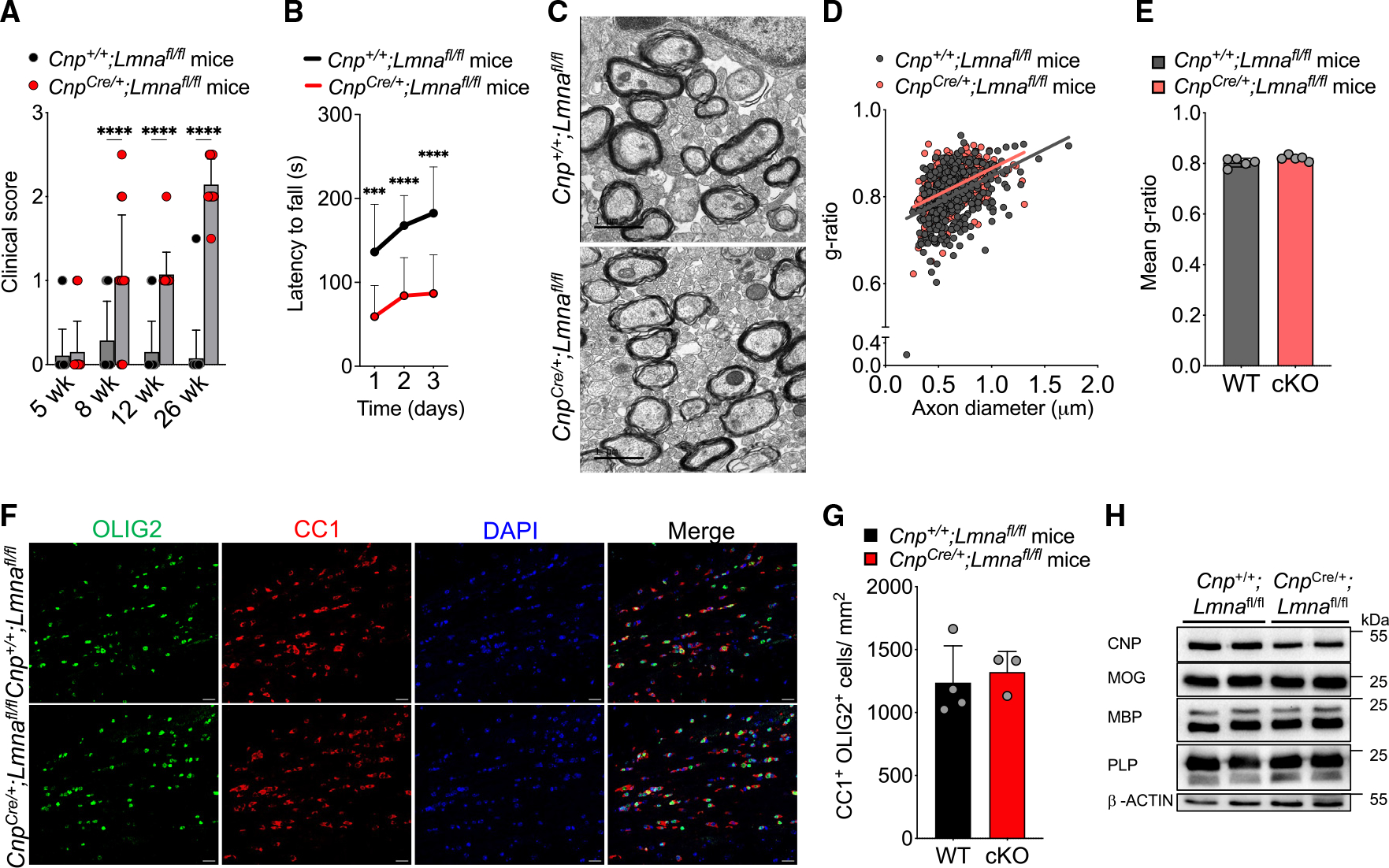
(A) Scatterplot of the clinical score observed in WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl) and Lmna mutant (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl) mice at 5, 8, 12, and 26 weeks. Data represented as mean + SD; WT mice: n = 19 at 5 weeks, 14 at 8 weeks, 20 at 12 weeks, and 20 at 26 weeks; Lmna mutant mice: n = 20 at 5 weeks, 14 at 8 weeks, 14 at 12 weeks, and 14 at 26 weeks (****p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA).
(B) Latency to fall in the rotarod test at 26 weeks in WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl; n = 18) and Lmna mutant mice (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl; n = 13) tested on 3 consecutive days. Data represented as mean ± SD (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA).
(C) Representative electron microscopy images of the myelinated axons in the corpus callosum of P21 WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl) and Lmna mutant mice (CnpCre/+; Lmnafl/fl). Scale bar, 1 μm.
(D) Scatterplot of g-ratios of myelinated axons presented as a function of axon diameter in WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl) and Lmna mutant (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl) P21 mice. Totals of n = 432 axons in 5 WT and 398 axons in 5 Lmna mutant mice were measured (WT, slope = 0.122 ± 0.014, intercept = 0.726 ± 0.009; cKO, slope = 0.120 ± 0.012, intercept = 0.745 ± 0.008).
(E) Scatterplot of the average ± SD g-ratio in the corpus callosum of WT and Lmna mutant P21 mice; n = 5 mice per genotype (p ≥ 0.05, two-tailed Student’s t test).
(F) Representative confocal images of the corpus callosum of WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl) and Lmna mutant mice (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl). Sections were stained with OLIG2 (green) and CC1 (red) antibodies. DAPI (blue) was used as counterstain. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G) Scatterplot of the number of CC1+/OLIG2+ cells per mm2 corpus callosum in WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl, n = 4) and Lmna mutant (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl, n = 3) mice. Data are represented as average ± SD (p ≥ 0.05, two-tailed Student’s t test).
(H) Western blot of protein extracts from spinal cord lysates of WT (Cnp+/+;Lmnafl/fl, n = 2) and Lmna mutant mice (CnpCre/+;Lmnafl/fl, n = 2), probed for the myelin proteins indicated on the left. Molecular weights indicated on the right. β-Actin was used as loading control.
