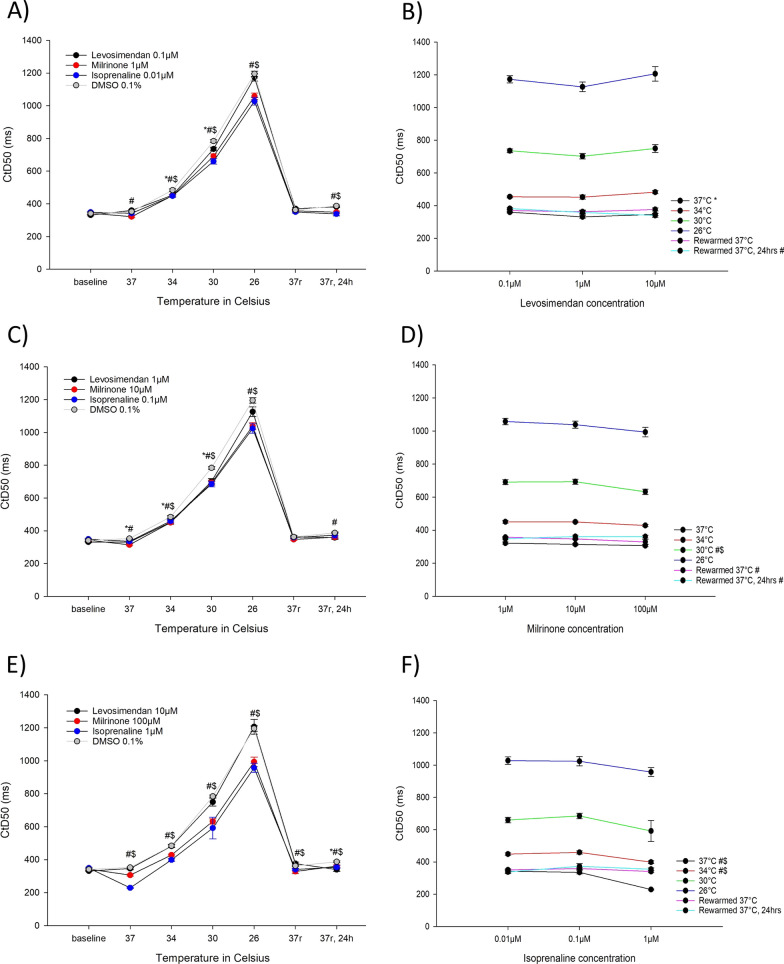
Fig. 6.
A Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the lowest concentrations of levosimendan (0.1 µM, n = 9), milrinone (1 µM, n = 9) and isoprenaline (0.01 µM, n = 9) during hypothermia and rewarming. B Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the different levosimendan concentrations (0.1 µM, 1 µM and 10 µM). C Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the intermediate concentrations of levosimendan (1 µM, n = 9), milrinone (10 µM, n = 9) and isoprenaline (0.1 µM, n = 9) during hypothermia and rewarming. D Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the different milrinone concentrations (1 µM, 10 µM and 100 µM). E Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the highest concentrations of levosimendan (10 µM, n = 9), milrinone (100 µM, n = 9) and isoprenaline (1 µM, n = 9) during hypothermia and rewarming. F Contraction duration, CtD50 (ms), for the different isoprenaline concentrations (0.01 µM, 0.1 µM and 1 µM). A, C, E *Significant differences between levosimendan and DMSO 0.1% (n = 15), #significant difference between milrinone and DMSO 0.1% (n = 15), $significant difference between isoprenaline and DMSO 0.1% (n = 15). B, D, F *Significant difference between lowest and intermediate concentration, #significant difference between lowest and highest concentration, $significant difference between intermediate and highest concentration