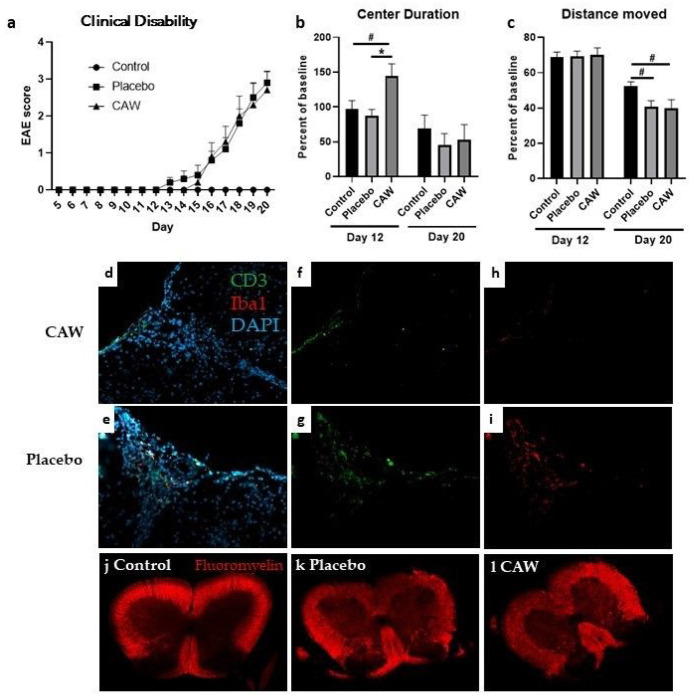
Figure 1.
a. Onset and final clinical disability in CAW-treated mice and placebo-treated mice following induction of experimental autoimmune encephalopathy (EAE) were similar between groups in Study 2. Control mice without EAE did not exhibit clinical disability b. Center Duration as a percent of baseline was greater in CAW-treated mice (less anxiety) than placebo or control cohorts at day 12 (early symptomatic) but not at Study 2 end. c. Distance Moved (activity) at Study 2 day 20 was lower in both CAW and placebo group compared to controls, likely reflecting disability caused by EAE. d., e. Composite stains for CD3 (green, lymphocytes) and Iba1 (red, activated microglia) are shown with DAPI (blue, DNA) in a CAW and placebo-treated mouse. f., g. Decreased CD3 staining for in a CAW-treated mouse compared to placebo. h., i. A trend toward decreased Iba1 staining for activated microglia between CAW and placebo-treated mice. j., k., l. While both EAE spinal cord sections demonstrate demyelination compared to control, there were no qualitative difference between placebo and CAW