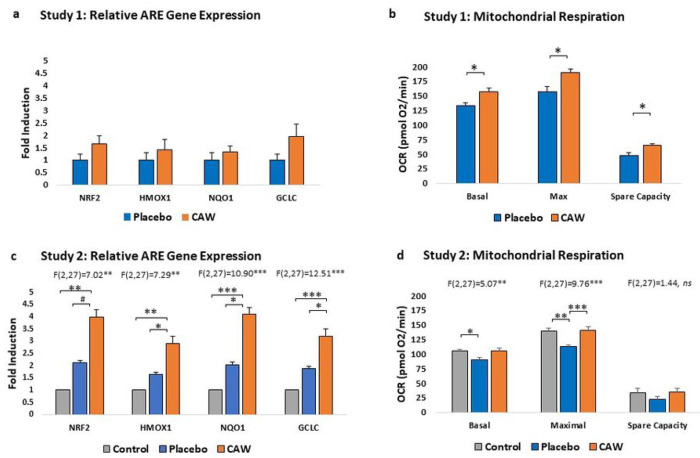
Figure 2.
a. Study 1: Greater, but non-significant, induction of antioxidant response element (ARE) gene expression in cerebral cortices of CAW-treated mice than placebo (n=4 per group). b. Mitochondrial respiration measured as oxygen consumption rates (OCR) of CAW-treated mice were significantly greater than placebo at basal, maximal, and spare capacity endpoints in Study 1. c. Study 2: ARE gene expression was significantly greater in CAW- compared to placebo-treated mice. Greater ARE gene induction in placebo than control mice reflect the compensatory antioxidant response to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. d. Study 2 additionally demonstrated normalization of mitochondrial respiration in CAW mice to those of controls without EAE. Pairwise differences in OCR between CAW and placebo in Study 2 reached significance at the maximal endpoint. HMOX1, heme oxygenase 1; GCLC, glutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit; NQ01, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase-quinone oxidoreductase 1; NRF2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, #p<0.10