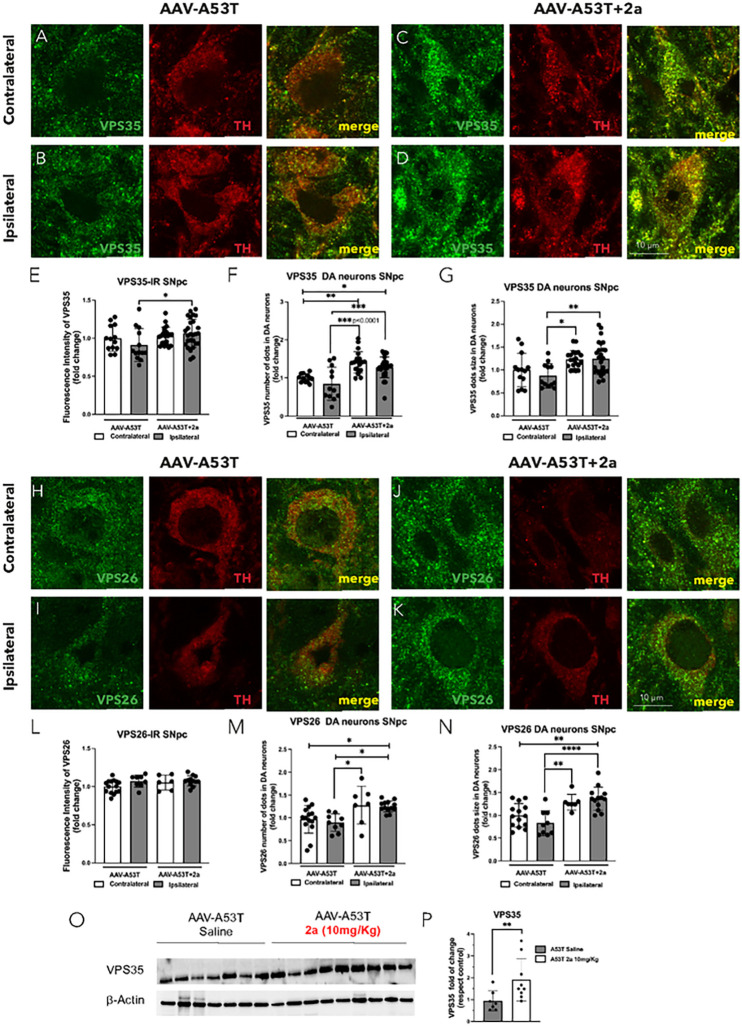
Figure 4. The pharmacological chaperone 2a increases retromer subunit protein immunoreactivity (IR), number of puncta and puncta size in DA neurons of the SN in AAV-A53T mice:
A-D) Double immunofluorescence of VPS35 (green) in TH-positive neurons (red) in the contralateral and ipsilateral SNpc of AAV-A53T injected mice treated with saline (A-B), or 2a (C-D), magnification 240X and scale bar is 10 mm; E-G) relative quantification of VPS35 fluorescence intensity (fold change) (E), number of VPS35 puncta where each dot represents an individual DA neuron in the SNpc (F) and VPS35 puncta size (G); H-K) Double immunofluorescence of VPS26 (green) in TH-positive neurons (red) in the contralateral and ipsilateral SNpc of AAV-A53T injected mice treated with saline (H-I), or 2a (J-K), magnification 240X and scale bar is 10 mm; L-N) relative quantification of VPS26 fluorescence intensity (fold change) (L), number of VPS26 puncta (M) and VPS26 puncta size (N); for these analyses we used 4–8 mice 3 fields each. O-P) Immunoblot analysis of VPS35 fold change in ipsilateral SN of AAV-A53T mice daily IP injected with 2a (10 mg/Kg) or saline for 100 days normalized to b-Actin protein levels and relative densitometric analysis; for this analysis (n=7–9 mice per group). Significance determined by one-way ANOVA. Error bars represent mean ± SD.