Figure 1.
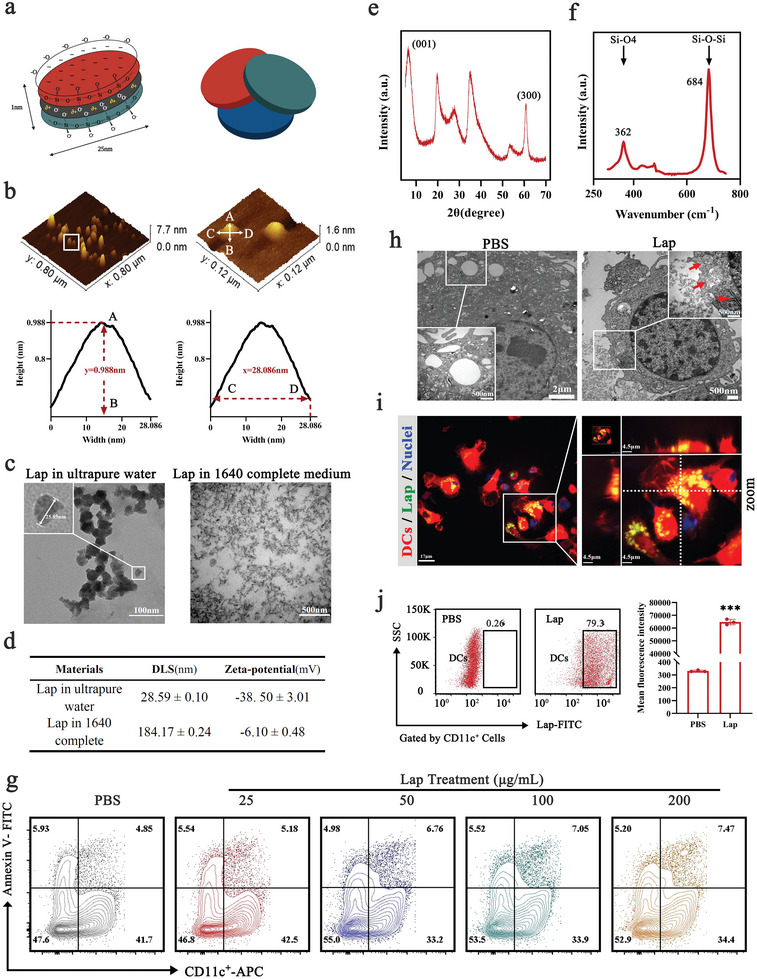
Characterization of Laponite (Lap) and its interaction with dendritic cells (DCs). a) Schematic of the layered structure of Lap. b) Atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of Lap. c) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of Lap dispersion in water or RPMI‐1640 culture medium. d) Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential of Lap in different dispersions. e) X‐ray diffraction pattern of Lap. f) Fourier transform‐Raman spectra of Lap from 250 to 800 cm−1. g) Membrane integrity of DCs treated with Lap at a dose of 25–200 µg mL−1. h) TEM images of Lap‐treated DCs. The red arrows in the zoomed graph show the formation of phagocytic cups with intracellular transport of Lap. i) Confocal images of Lap locations in DCs. Red: DCs from tdTomato fluorescent protein transgenic mice; Green: fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)‐labeled Lap; blue: nuclei. j) Detection of Lap colocalized in DCs with flow cytometry (FCM). Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). ***P < 0.001 compared with the phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS) group. Representative results from two or three replicates are shown.
