Figure 2.
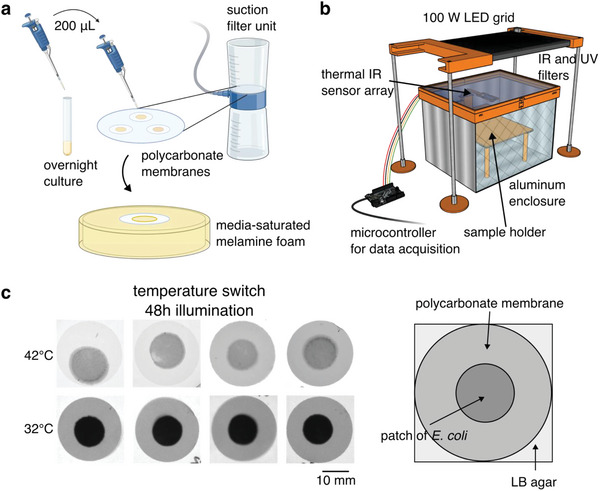
Temperature‐dependent pigmentation in a model ELM. a) Schematic of formation of dense, centimeter‐scale patches of E. coli to simulate the ELM environment. We grew E. coli overnight to saturation in a liquid medium. For each patch, we transferred 200 µL of culture to track‐etched polycarbonate membranes (25 mm diam., 0.2 µm pores) and applied suction to coat the cells onto the membranes, forming a dense patch. We then transferred the coated membranes to a melamine foam substrate saturated with liquid media for growth. b) Schematic of illuminated growth chamber. We used a 100 W white light LED to expose E. coli patches to illumination and monitored the temperature using a 32 × 24 array of thermal IR sensors. The sensor array is attached to a motorized arm and retracts when not imaging to avoid shadowing the samples. c) Transillumination white light images of patches of E. coli containing the temperature switch construct on polycarbonate membranes after 48 h growth in the illuminated growth chamber with pigment‐induction media at 42 °C and 32 °C. Parts of figure created with BioRender.com.
