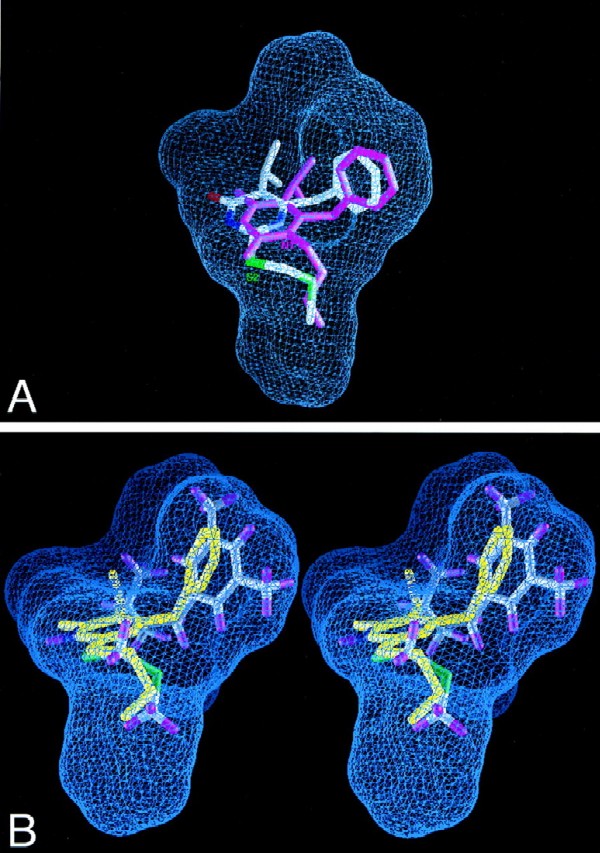
FIG. 2.
View of composite NNI binding pocket of HIV-1 RT. Blue grid lines represent the collective van der Waals surface of nine different inhibitor crystal structures superimposed on the active site and highlight the space available for binding (inhibitor structures included HEPT, MKC, TNK, APA, nevirapine, N-ethyl nevirapine derivative, 8-Cl TIBO, and two 9-Cl TIBO compounds with PDB access codes 1rti, 1rt1, 1rt2, 1hni, 1vrt, 1rth, 1hnv, 1rev, and 1tvr, respectively). (A) Compound 3c superimposed on the composite NNI binding site of the crystal structure of the RT-MKC442 complex (hydrogen atoms are not shown; PDB access code, 1rt1). MKC442 (from crystal structure) is shown in pink, and compound 3c (from docking calculations) is multicolored. Compound 3c was docked into the active site of the RT-MKC442 complex and then superimposed onto the composite NNI binding pocket based on the matrix used in pocket construction. The S2 substituent of DABO analog 3c occupies the same region of the binding pocket as the N1 substituent of HEPT analog MKC442. (B) X-ray crystal structure of compound 3b (yellow) superimposed on the docked model of compound 3d in the composite NNI binding pocket of RT, demonstrating their similar conformations.