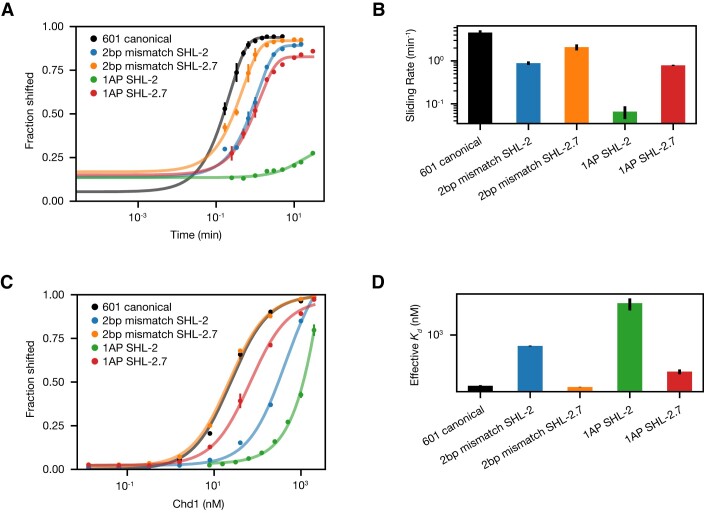
Figure 6.
Chd1 sliding activity and binding are most strongly affected by DNA perturbations at SHL-2. (A) Quantification of nucleosome sliding reactions, using 80N0 nucleosomes with the indicated defect at either SHL-2 or SHL-2.7. Shown are the means plus standard deviations from three replicates. Lines show the best single exponential fits. (B) Nucleosome sliding rates, based on fits shown in (A). Rates (min−1) were calculated to be 4.6 ± 0.6 (601 canonical); 0.89 ± 0.09 (2 bp mismatch, SHL-2); 2.1 ± 0.3 (2 bp mismatch, SHL-2.7); 0.07 ± 0.02 (1AP SHL-2); and 0.79 ± 0.02 (1AP SHL-2.7). For each construct, the average value was determined from three or more reactions, with error bars indicating standard deviations. (C) Binding titrations for nucleosomes shown in (A), carried out in the presence of AMP-PNP and salmon sperm DNA. (D) Observed binding affinities as shown in (C). Observed Kd values (nM) were calculated to be 24 ± 1 (601 canonical); 450 ± 15 (2 bp mismatch, SHL-2); 22.2 ± 0.3 (2 bp mismatch, SHL-2.7); 10 000 ± 4000 (1AP SHL-2); and 68 ± 12 (1AP SHL-2.7). Binding reactions were performed three or more times, with error bars indicating the standard deviations of fit values. Representative gels for sliding and binding reactions are shown in Supplementary Figure S6.