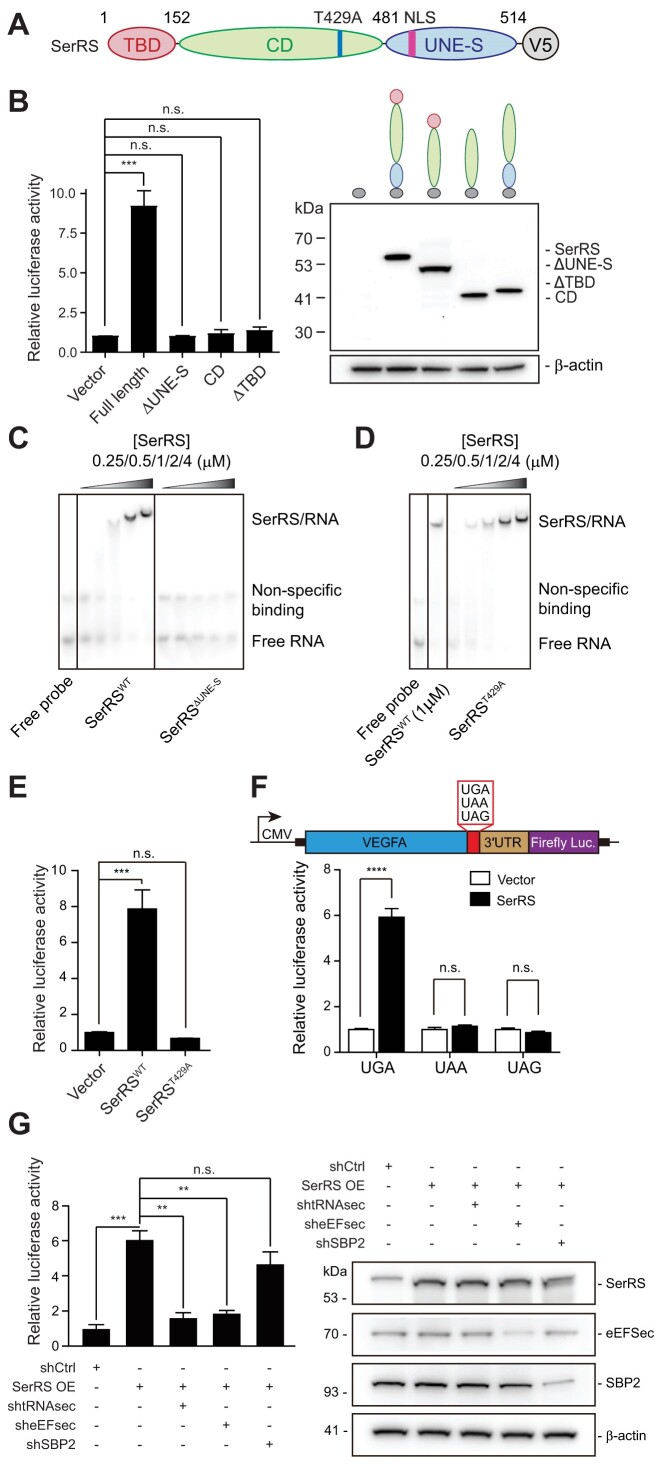
Figure 2.
SerRS-mediated translational readthrough is dependent on SerRS catalytic activity and selenocysteine incorporation elements. (A) Scheme of SerRS domain structure. (B) Domain mapping for SerRS-mediated translational readthrough. SerRS contains a tRNA-binding domain (TBD), a catalytic domain (CD) and a domain unique to SerRS (UNE-S) involved in nucleic acid binding. Expression of V5-tagged SerRS domains was confirmed by western blot. (C) EMSA showing binding of SerRSWT but not SerRSΔUNE-S to the VEGFA mRNA. (D) EMSA showing binding of the catalytic mutant SerRST429A to the VEGFA mRNA. (E) A point mutation in the SerRS catalytic site (T429A), which renders SerRS catalytically inactive, abolished SerRS translational readthrough activity. (F) Mutation of the UGA stop codon to UAA or UAG abrogated increased translational readthrough upon SerRS overexpression in a VEGFA-based luciferase reporter assay. (G) SerRS-mediated TR measured by a VEGFA reporter assay with SerRS overexpression. TR is dependent on tRNASec and eEFSec, as their knockdown abrogates the increase in translational readthrough by SerRS overexpression. SBP2 knockdown does not affect TR. Knockdown was verified by western blot. (A–G) (n.s., not significant; ** P< 0.01; *** P< 0.001; **** P< 0.0001)