FIGURE 3.
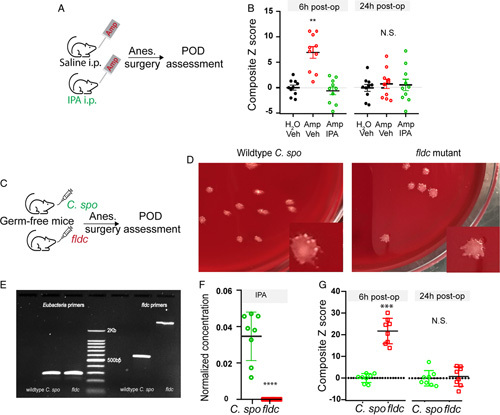
IPA is critical for POD. (A, B) Exogenous IPA administration protects against POD development. (A) Flowchart: mice were fed on water supplemented with ampicillin, and received saline or IPA i.p. injection twice daily for 14 days. After A/S, behavior tests were performed to assessor for POD. (B) Behavior composite Z score at 6- and 24-hour postoperatively. For each time point, comparison of the groups was carried out using 1-way ANOVA, post-hoc LSD test was performed where appropriate. N=10 each group. **P<0.01 “Amp, Vehicle” versus “Amp, IPA”. N.S., P>0.05 with 1-way ANOVA, no post-hoc analysis was performed. (C–G) Mutant Δfldc strain promotes POD-like behavior in germ-free mice. Wild-type Clostridium sporogenes and mutant Δfldc strain were used to colonized germ-free mice (N=8 each group). Two weeks later, mice underwent anesthesia-surgery followed by behavioral testing. (C) Flowchart of experimental design. (D, E) Confirmation of colonization. Fecal pellets were dissolved in sterile PBS follow by culture (D) or PCR (E). (D) Forty eight to 72 hours after plating, shown representative picture of each group demonstrating one type of colony shape for mice colonized with wild-type C. sporogenes or mutant Δfldc strain. E) PCR confirmation of colonization. Fecal DNA was amplified with 2 sets of PCR primers: one for all eubacteria; the other set (fldc primers) distinguishes wild-type C. sporogenes or mutant fldc strain. For the fldc primers, wild-type C. sporogenes yields a band at ~600 bp, whereas fldc mutant yields a band at 2.3 Kb. (F) Plasma IPA concentration from germ-free mice received wild-type C. sporogenes or mutant Δfldc strain. ****P<0.0001, t test. (G) Behavior composite Z score at 6- and 24-hour postoperatively. **P<0.01, N.S. P>0.05, t test. ANOVA indicates analysis of variance; A/S, anesthesia-surgery; IPA, indole-3-propionic acid; LSD, Fisher’s least significant difference; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; POD, postoperative delirium.
