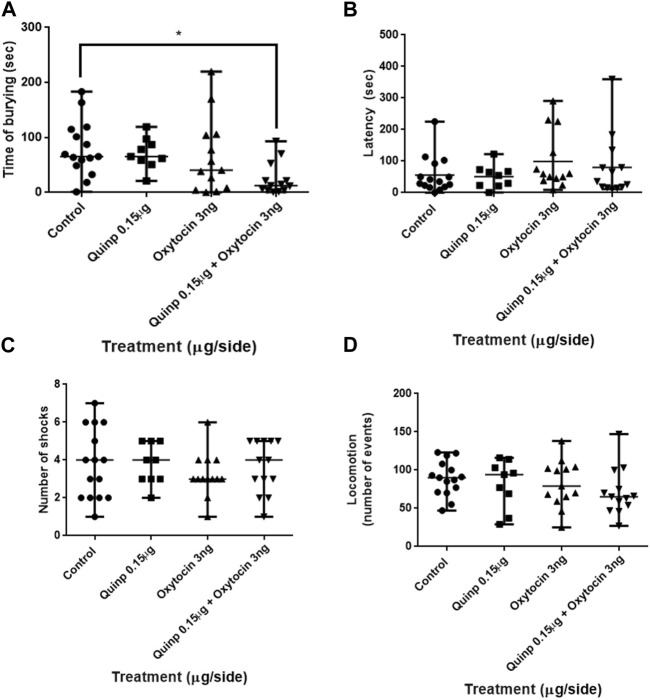
FIGURE 3.
Effects of the co-administration of oxytocin and quinpirole into the central amygdala in the shock-probe burying test and of the locomotion in the open-field test. (A) Co-infusion of quinpirole (Quinp) (0.15 μg) + oxytocin (3 ng) evoked a marked decrease in the time that animals spent burying the probe of the test versus that of the control group. No effects on (B) the latency to the first episode of burying and (C) on the number of shocks that the rats received during the test were observed. (D) No significant differences in the locomotor activity of any treated group were observed as compared to the control. The Kruskal–Wallis test was followed by the Dunn test. *p < 0.05. Control: n = 15; quinpirole 0.15 µg/side: n = 9; oxytocin 3 ng/side: n = 13; quinpirole 0.15 µg + oxytocin 3 ng/side: n = 13.