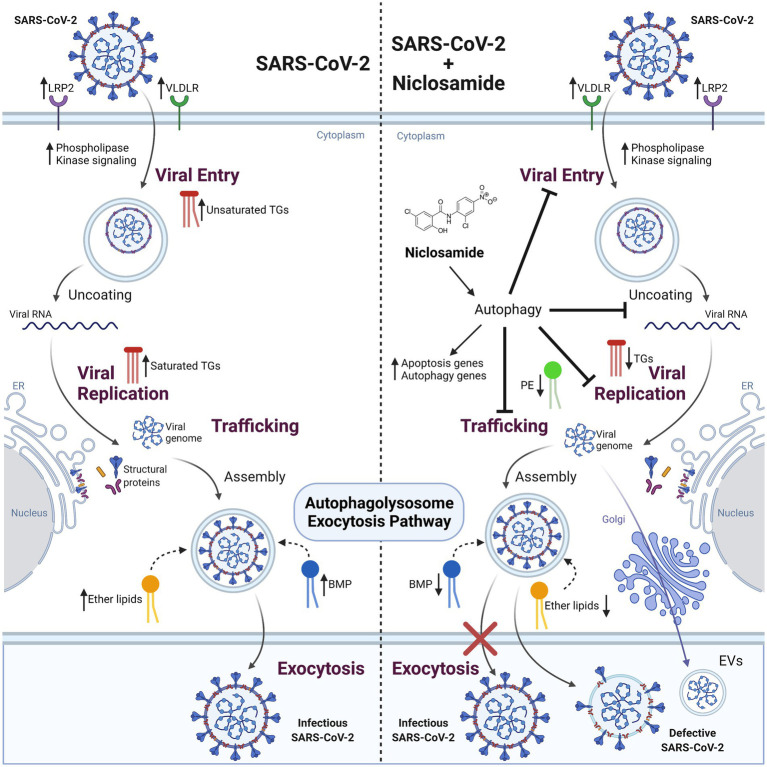
Figure 8.
The effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection and NIC treatment on host cell lipid metabolism. SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero E6 cells alters host cell lipid metabolism during early and late stages of infection. Increased transcription of lipid receptors LRP2 and VLDLR, and phosphorylation signaling regulators are observed throughout viral infection. Changes in TG composition from unsaturated to saturated acyl-chains occur as a function of viral replication, with an overall decrease in TG lipids at late infection timepoints. This change corresponds with an increase to DG and BMP lipids that is indicative of energy consumption and incorporation into membranes and vesicles, activation of autophagy pathways, as well as impacting viral replication. Treatment of cells with NIC alters lipid composition and gene regulation corresponding to apoptosis and autophagy related pathways. Decreases to ether lipids (TGs and DGs) and BMP are observed and reflect a decrease to exocytosis pathways for viral egress. Created with BioRender.com.