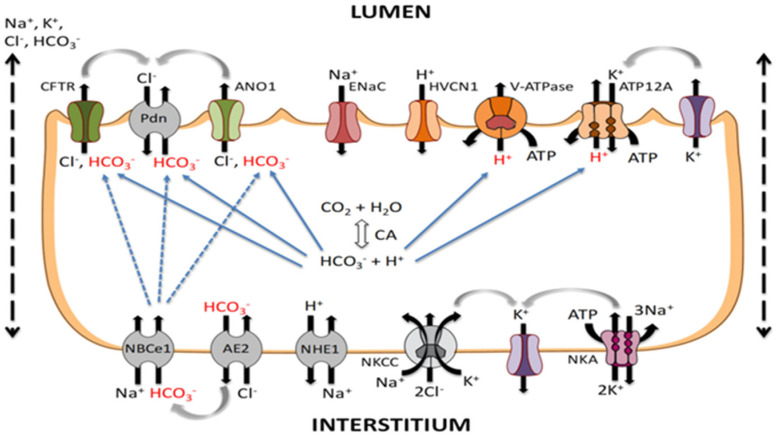
Figure 1.
Ion transport across alveolar epithelial cells. Na+ and Cl− ions enter the apical membranes (lumen) of alveolar epithelial cells (both Type I and Type II) via Epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) and Cl− channels such as cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) located in the apical face of the cell (interstitium). The Na+ ions are driven by an electrochemical gradient created by the energy-dependent Na/K-ATPase. K+ ions, brought in by the Na/K-ATPase pump in exchange for the Na+ ions, leave the cell passively through K+ channels located in the basolateral membrane. CFTR: Cystic fibrosis transport regulator; ENaC: Epithelial sodium channel.