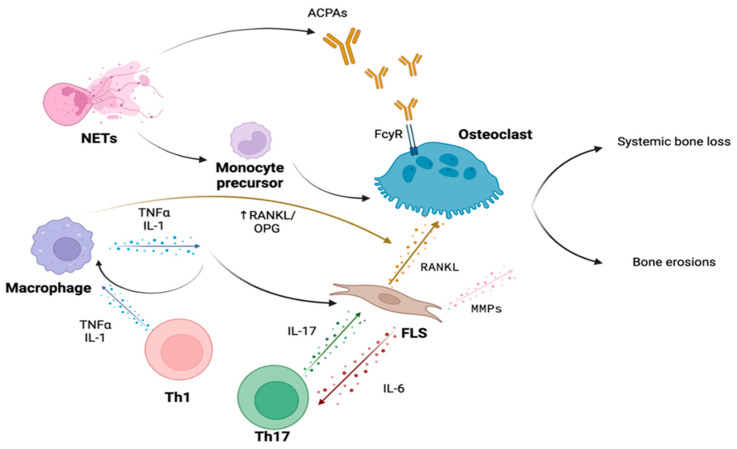
Figure 1.
Cellular and molecular interplay involved in the pathogenesis of bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis. ACPAs, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand; OPG, osteoprotegerin; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; FLS, fibroblast-like synoviocytes; NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; FcγR, fc gamma receptor; IL-1, interleukin-1; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-17, interleukin 17.