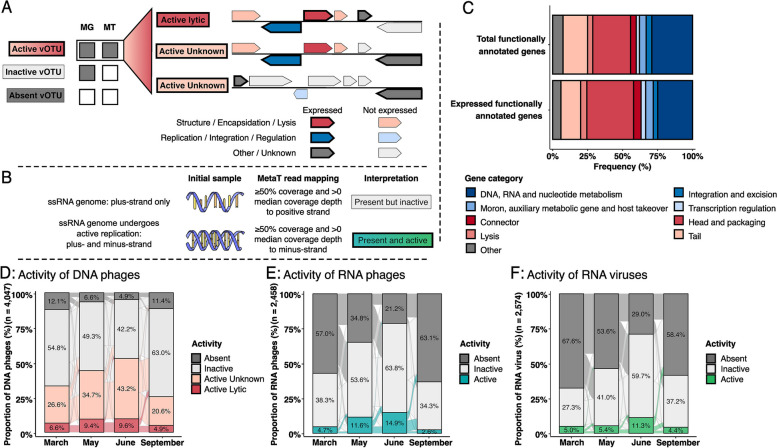
Fig. 4.
Functional annotation and activity of DNA and RNA viruses. A Schematic representation of the framework used for assessing the activity, including the infection stage, of DNA phages. Metatranscriptome read mapping is used to identify expressed genes in each viral DNA vOTU, and the number and annotation of these genes are then used to determine the activity and the infection stage of each DNA vOTU. DNA phages for which at least one expressed gene was detected were classified as active (Supplementary Fig. 2). B Schematic representation of the framework used for assessing the activity of ssRNA viruses. Based on metatranscriptome read mapping, ssRNA viruses are classified as actively replicating if both coding and non-coding genome strands are detected and considered as “present” if only the coding strand is detected. C Proportion of total and expressed annotated genes based on functional annotation using Prokka v1.14.6 from DNA viral genomes by aligning them against PHROGS v4 database, with an e value cutoff 1E − 6. Functional categories associated with lytic infections, i.e., categories associated with virion production and host cell lysis, are colored in red, and the other major phage functional categories are colored in blue. Only genes that were annotated are included in the figure, and the proportion of annotated genes over all genes in the (active) DNA vOTUs is indicated next to each bar chart. D Proportion of active (dark and light red), inactive (light gray), and absent (dark gray) DNA phages across months. Within DNA vOTUs identified as active, the ones likely engaged in active lytic infection were identified based on the functional annotation of expressed genes, while other active vOTUs are identified as “active—unknown.” The spaces between the different branches represent the transition (or connection) of each vOTU between categories. E, F Proportion of active (blue and green), inactive (light gray), and absent (dark gray) RNA phages (E) and RNA viruses (F) across months. A vOTU is considered as active when it is detected as active in at least one sample. Transcriptional activity is measured by read mapping from at least one metatranscriptome to at least one gene of the vOTU (Supplementary Fig. 1). The proportion of active vOTUs for each month is the sum of all active vOTUs for a given month