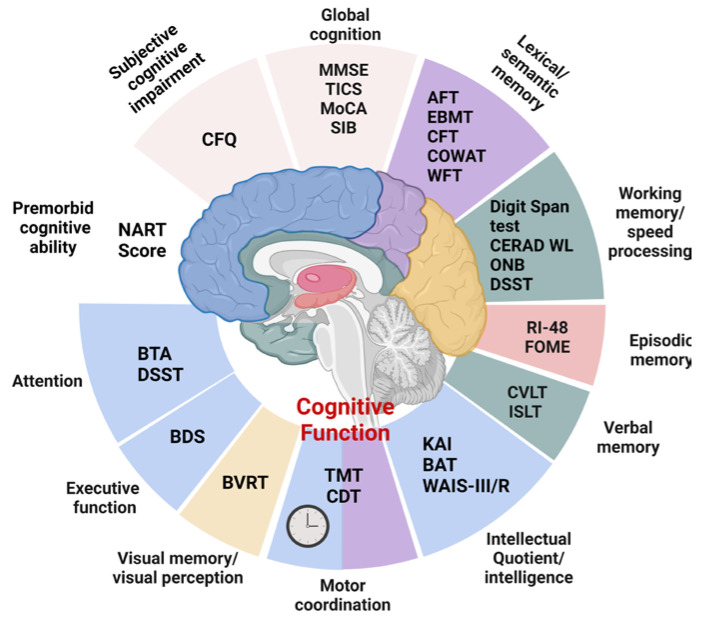
Figure 3.
Scheme of the cognitive test batteries and assessment tools used in the systematically revised literature. Global cognition was assessed with the following: MMSE: mini-mental state examination; TICS: Telephone Interview of Cognitive Status; MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment; SIB: Severe Impairment Battery. Lexical/semantic memory was assessed with the following: AFT: Animal Fluency Test; EBMT: East Boston Memory Test; CFT: Category Fluency Test; COWAT: Controlled Oral Word Association Test; WFT: Word Fluency Test. Working memory/speed processing was assessed with the following: the digit span test; CERAD WL: Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease Word Learning; ONB: One Back Task; DSST: Digit Symbol Substitution Test. Episodic memory was assessed with the following: RI-48: Cued Recall Test; FOME: Fuld Object Memory Evaluation. Verbal memory was assessed with the following: CVLT: California Verbal Learning Test; ISLT: International Shopping List Task. Intellectual quotient/intelligence was assessed with the following: KAI: Kurztest fuer Allgemeine Intelligenz; BAT: Berliner Amnesie Test; WAIS-III: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Revised. Motor coordination was assessed with the following: TMT, Trail Making Test; CDT: Clock Drawing Test. Visual memory/visual perception was assessed with the BVRT: Benton Visual Retention Test. Executive function was assessed with the BDS: Behavioral Dyscontrol Scale. Attention was assessed with the following: BTA: Brief Test of Attention; DSST: Digit Symbol Substitution Test. Premorbid cognitive ability was assessed with the NART: National Adult Reading Test. Subjective cognitive impairment was assessed with the CFQ: Cognitive Failures Questionnaire. The visualization was created with BioRender.