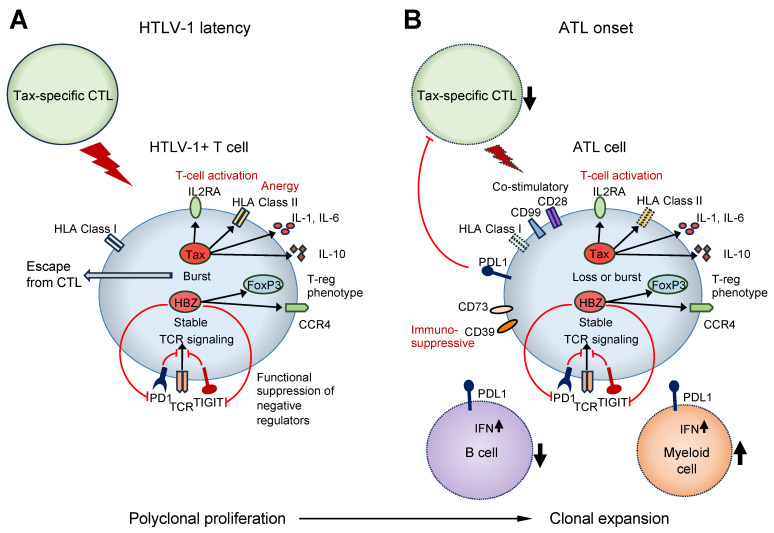
Figure 1.
Summary of the immune pathologies during HTLV-1 latency and onset of ATL. (A) In asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers, the proliferation of HTLV-1-infected T cells and their clearance by CTLs are in equilibrium. HTLV-1 transiently expresses Tax and affects the expression and function of immune-related molecules to evade host immunity and promote survival of HTLV-1-infected cells. (B) Patients with ATL develop immunodeficiency; however, ATL cells also accumulate genetic abnormalities in immune-related genes, and clones that are advantageous for escaping host immunity are selected for extensive proliferation. In addition to CD4+ T cells, decreased numbers of CTLs and B cells, increased numbers of myeloid cells, and decreased NK cell function are observed. HTLV-1, Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1; ATL, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; CTL, cytotoxic T cell.