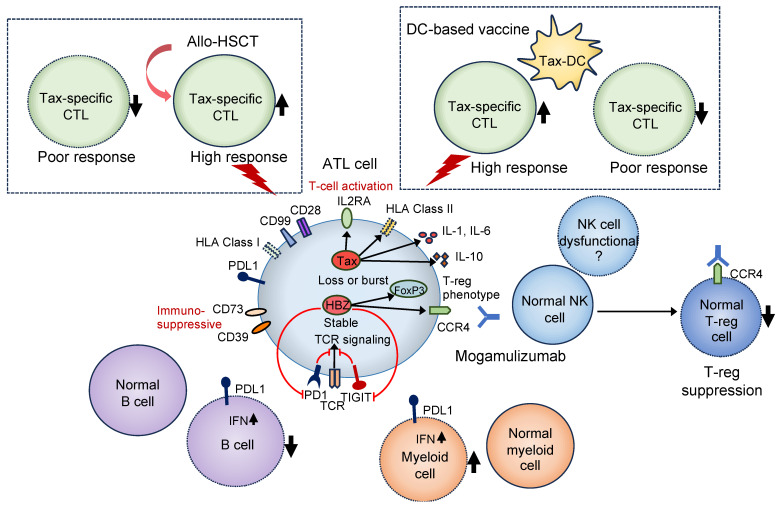
Figure 2.
Relationship between immune pathology and therapeutic efficacy in patients with ATL. As the therapeutic effects of allo-HSCT and Tax-dendritic cell vaccine therapy depend on the activity of Tax-specific CTLs, the presence of functional CTLs is indispensable. Characterization of circulating ATL cells may be important as CTL decline is also associated with genomic abnormalities in ATL cells, such as PD-L1 [61]. Mogamulizumab suppresses not only ATL cells but also regulatory T cells (Treg). The antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic effect of mogamulizumab depends on the activity of NK cells and may be less effective in some patients with ATL, owing to decreased NK cell function [61,70]. Dotted lines in boxes indicate the hypotheses. ATL, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; allo-HSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; CTL, cytotoxic T cell; NK, natural killer cell; DC, dendritic cell.