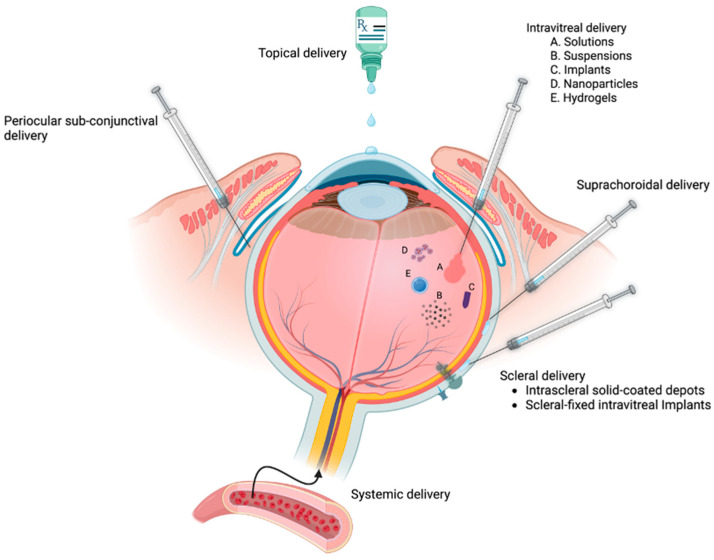
Figure 5.
Various ocular delivery routes for anti-inflammatory GCs. Topical ocular delivery is used to treat the ocular surface and anterior segment. Drug depots can be placed adjacent to the eye by periocular sub-conjunctival injections, superchoroidal injections or intrascleral injections. Intraocular delivery is often used to treat posterior segment tissues (e.g., retina) by the intravitreal injections of solutions, suspensions, biodegradable implants, nanoparticles, or hydrogels. In addition, there are delivery devices that are surgically implanted and tethered to the sclera. Systemic delivery is sometimes used for sight-threatening inflammation, but the GCs must transit the natural blood–aqueous barrier and blood–retinal barrier (which is sometimes compromised during ocular inflammation). Figure created using BioRender.