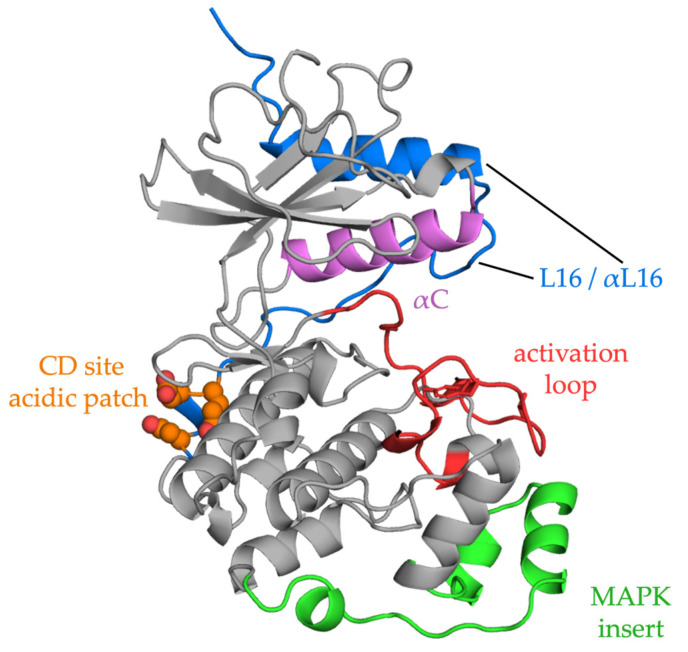
Figure 2.
ERK2 structure. The ribbon diagram shows the two-domain structure of ERK2. Activation of the kinase occurs upon phosphorylation of the TEY motif in the activation loop (red), which lies in front of the active site. Phosphorylation causes a small domain closure, relative to other protein kinases. Reorganization of loop L16 (blue), part of a C-terminal extension that wraps up the back of the kinase, causes repositioning of alpha helix C (αC, magenta), allowing formation of a salt bridge between the glutamate in the helix to the essential lysine in beta strand 3 in the interior of the active site. The acidic residues that make up the CD domain are shown in orange. The FXF binding site lies between the MAPK insert (green) and the kinase core. Interactions through these two docking motifs may provoke conformational changes in ERK2 [115,116,117,118].