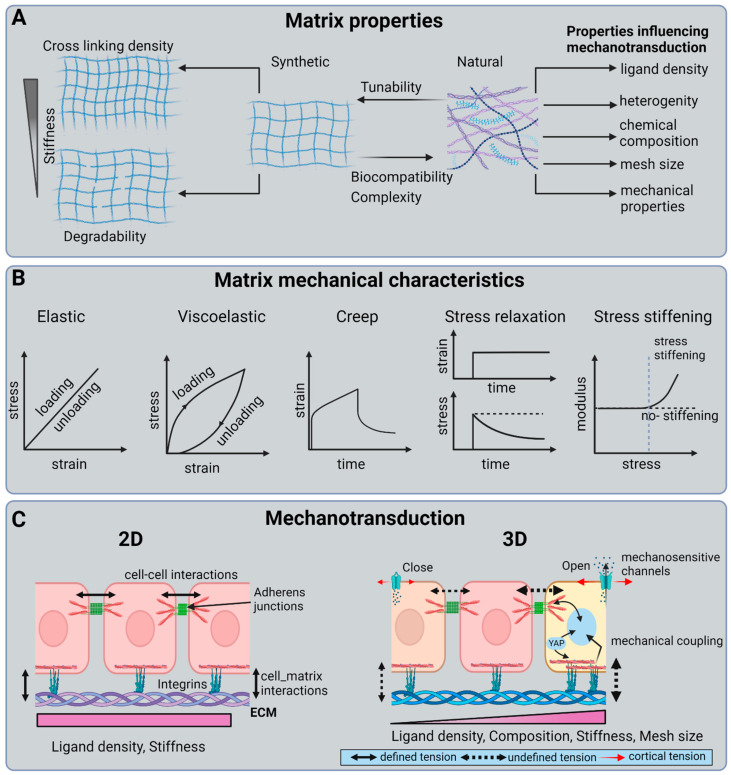
Figure 4.
Matrix composition, material properties, and mechanotransduction: (A) Matrix properties: Synthetic matrices are simple and allow matrix composition to be tuned to achieve specific mechanical properties. Natural hydrogels, on the other hand, are complex and hard to manipulate. (B) Matrix mechanical properties: an elastic material has a linear stress–strain response. That said, most hydrogels are nonlinear, i.e., viscoelasticity and non-linearity increases with increasing chemical complexity. (C) Mechanotransduction: mechanotransduction in 3D is more complex than in 2D. Cells in 2D sense uniform ligand density and substrate stiffness. In 3D, on the other hand, there is spatial variation in ligand density, composition, mesh size, and stiffness. Furthermore, cell populations exhibit heterogeneity and, hence, varying mechanical sensitivities.