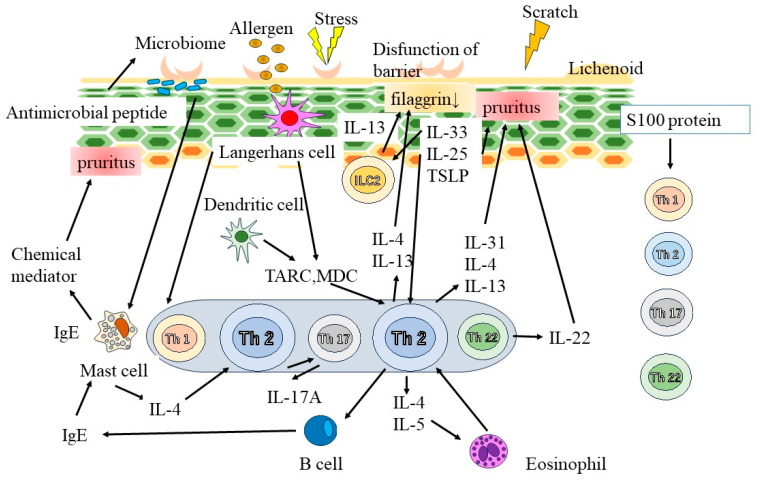
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis of AD. The primary components of the skin barrier are intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum, including ceramides. In addition, tight connections illustrate the adhesive structure between the epidermal cells which prevents foreign substrates from penetrating the skin. Chronic skin inflammation in AD is significantly affected by skin barrier dysfunction. Interleukin (IL)-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) are produced by epidermal keratinocytes and are responsible for type 2 immune response-mediated inflammation. Thymus- and activation-related chemokine (TARC) as well as macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC) are produced in atopic skin lesions and contribute to the migration of Th2 cells to skin lesions. IgE, immunoglobulin E.