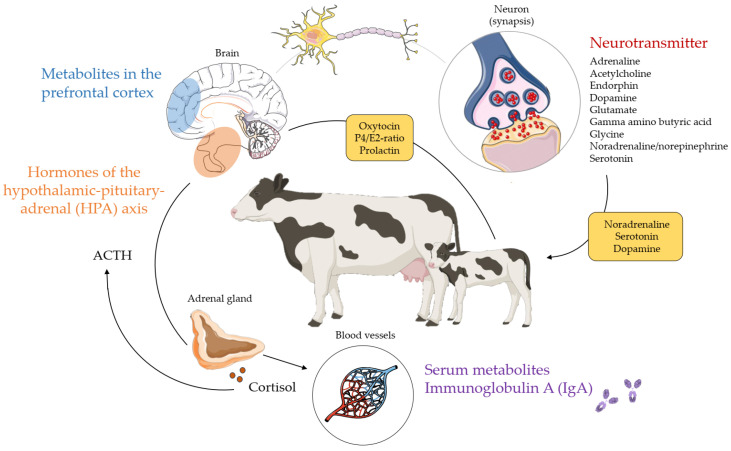
Figure 2.
Molecular biomarkers known to be involved in dairy cow behaviour. The complex of behaviour molecular biomarkers includes hormones of the HPA axis, metabolites in the prefrontal cortex, neurotransmitters, serum metabolites and circulating IgA. The hormone ACTA stimulates cortisol production in the adrenal gland. Simultaneously, increased cortisol concentration in plasma negatively regulates ACTH production by the pituitary gland. The neurotransmitters are synthesised and released by neurons and act within synaptic gaps to transmit signals between neurons. Some neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine, endorphin) act as both neurotransmitters and as hormones. Molecular biomarkers potentially involved in dairy cow maternal behaviour (verified in other animal species) are written in yellow boxes.