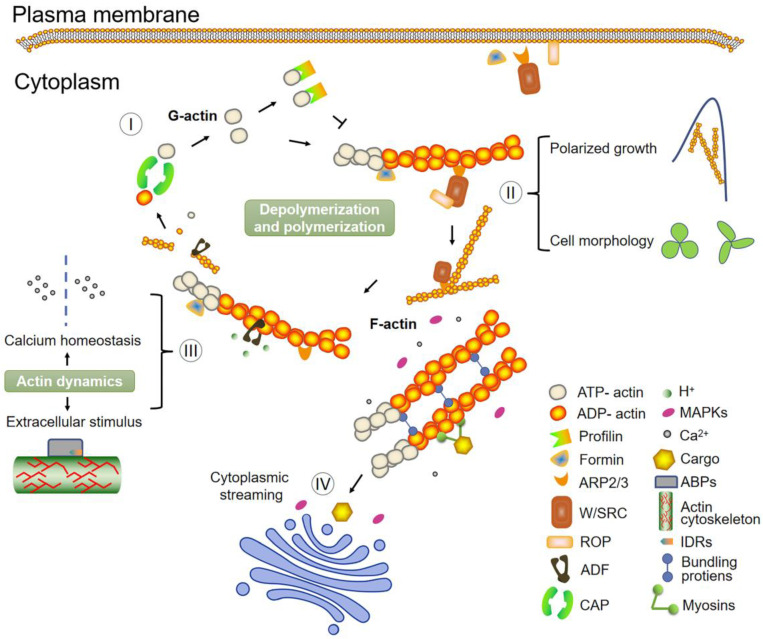
Figure 3.
Fundamental model depicting actin dynamics and various processes that involve the actin filaments. (I) The conversion from ADP-actin to ATP-actin is accomplished by CAP and is a strategic step that guarantees the polymerization cycle. The nucleation factors, like ARP2/3 and the formins, order the polymerization of the actin monomers (G-actin). Profilin can also bind actin monomers to maintain the actin monomer pool by inhibiting the polymerization of actin filaments. Generated actin filaments (F-actin) are bundled at different angles via binding proteins or crosslinkers. Any depolymerized actin filaments will re-enter the assembly system. (II–IV) The dynamic changes of the actin cytoskeleton participate in plant cell development through the functional association of different signaling pathways. Filamentous actin arrays are associated with plant cell growth, and the activity of ABPs is essential for proper cell morphogenesis. Cytoplasmic streaming plays a vital role in the transportation of materials necessary for tip elongation. Meanwhile, actin reorganization during cellular processes, such as polar growth and cytoplasmic streaming, is frequently correlated with calcium influxes or intracellular calcium gradients.