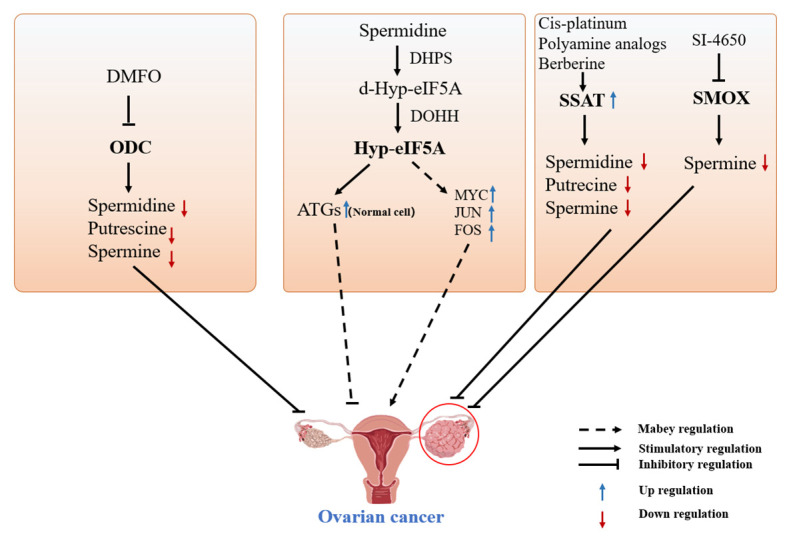
Figure 4.
Polyamine metabolism regulates the development of ovarian cancer. (Left) Inhibition of ODC, a key target of anabolic enzymes in polyamine metabolism, can hinder the development of ovarian cancer. (Middle) In normal cells, spermidine may regulate the translation of some autophagy-related genes by mediating hyp-eIF5A, thereby inhibiting the development of ovarian cancer. Spermidine may promote the development of ovarian cancer by regulating oncogene translation through hyp-eIF5A. (Right) Anticancer drugs inhibit the development of ovarian cancer by targeting the catabolic enzymes of polyamine metabolism, such as SSAT and SMO.