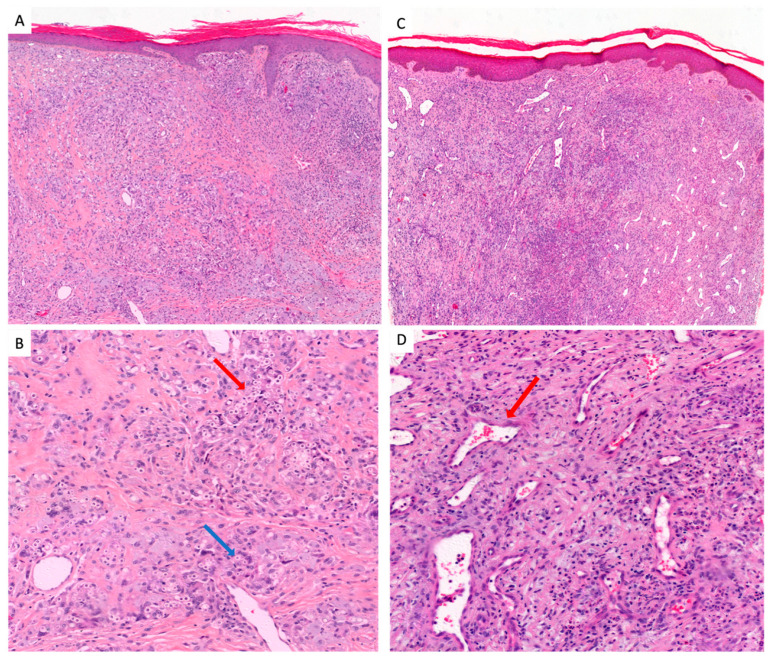
Figure 2.
The two histological types of lobomycosis. (A) Classic type: acanthosis and hyperkeratotic epidermidis, important inflammatory reactions. A milder inflammatory infiltrate is also seen in the center and periphery of the lesion, consisting of a few lymphocytes, plasma cells and rare eosinophils (HE-stain 10X). (B) Classic type: reaction of the dermis composed of multinucleated giant cells (blue arrow) and histiocytes with numerous round yeasts (red arrow), mostly intracellular with some extracellular yeasts (HE stain 40X). (C) Telangectatic scar type: the dermis is particularly fibrous and looks like a scar that delimits numerous dilated vessels (red arrow). The scar is punctuated by a moderate inflammatory infiltrate (HE-stain 10X). (D) Telangectatic scar type: a moderate inflammatory infiltrate consisting of histiocytes, lymphocytes and plasma cells with exceptional multinucleated giant cells with rare yeasts mostly intracellular but numerous dilated vessels showed by the red arrow (HE stain 40X).