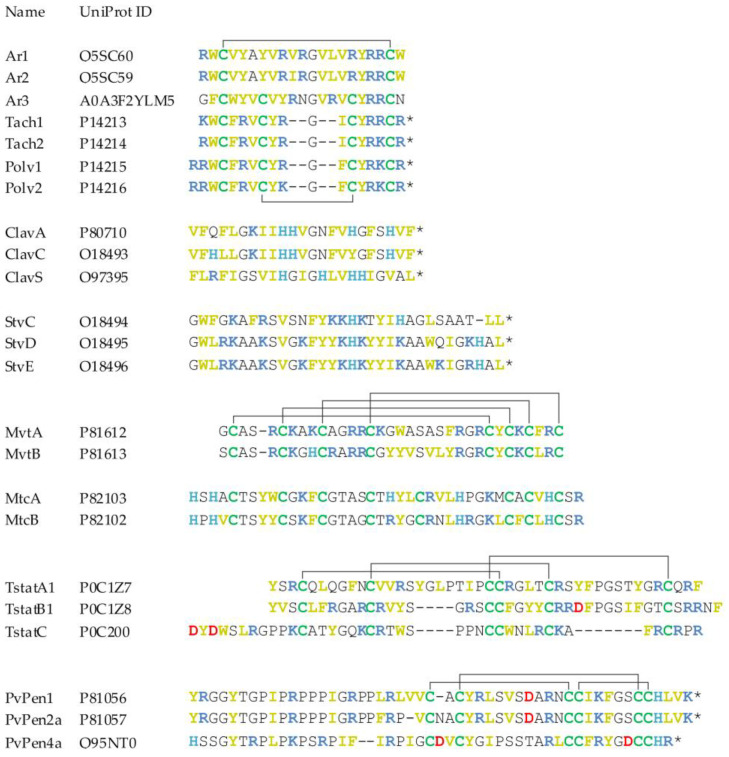
Figure 3.
Amino acid sequence alignments of several families of marine invertebrate HDPs. Ar1, Ar2, Ar3—arenicins-1, -2, -3 from Arenicola marina (lugworm); Tach1, Tach2—tachyplesins I and II from Tachypleus tridentatus (Japanese horseshoe crab); Poly1, Poly2—polyphemusins 1 and 2 from Limulus polyphemus (Atlantic horseshoe crab); ClavA, ClavC, ClavS, StyC, StyD, StyE—clavanins A, C, clavaspirin, and styelins C, D, E from Styela clava (Sea squirt); MytA, MytB—mytilins A and B from Mytilus edulis (Blue mussel); MtcA, MtcB—myticins A and B from Mytilus galloprovincialis (Mediterranean mussel); TstatA1, TstatB1, TstatC—tachystatins from T. tridentatus; PvPen1, PvPen2a, PvPen4a—penaeidins 1, 2a, 4a from Penaeus vannamei (Whiteleg shrimp). Basic residues (HKR) are shown in blue; acidic (D)—in red; highly hydrophobic (FILVWY)—in yellow; cysteine residues—in green. The arrangement of disulfide bonds and the amidated C-terminal residues (*) are shown. Other modifications, such as hydroxylated and brominated residues, are not shown in the figure.