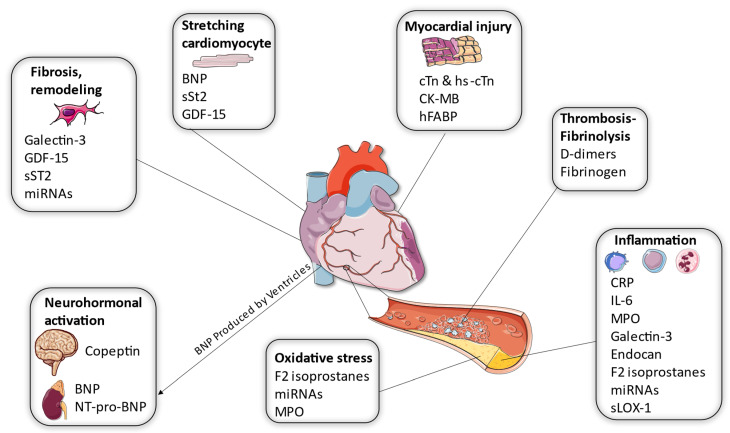
Figure 1.
Different roles of biomarkers in the pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction. The biomarkers for MI can be categorized based on their mechanism of action. Some are secreted by the cardiomyocytes, while others are correlated with inflammation, clot formation, and neurohormonal pathways. It is interesting to note that some biomarkers (galectin-3, miRNAs, BNP, sST2, and GDF-15) are included in more than one category, proving the multiplicity of their pathophysiology (BNP: B type natriuretic peptide; CK-MB: Creatine Kinase- MB; CRP: reactive protein; cTn: Cardiac Troponin; GDF-15: Growth Differentiation Factor-15; hFABP: Heart- Type Fatty Acid Binding Protein; MI: Myocardial Infarction; miRNAs: micro-RNAs; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; NT-proBNP: N-terminal portion of the pro-BNP peptide; sLOX-1: Soluble oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; sST2: Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity) Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/) (accessed on 16 September 2023).