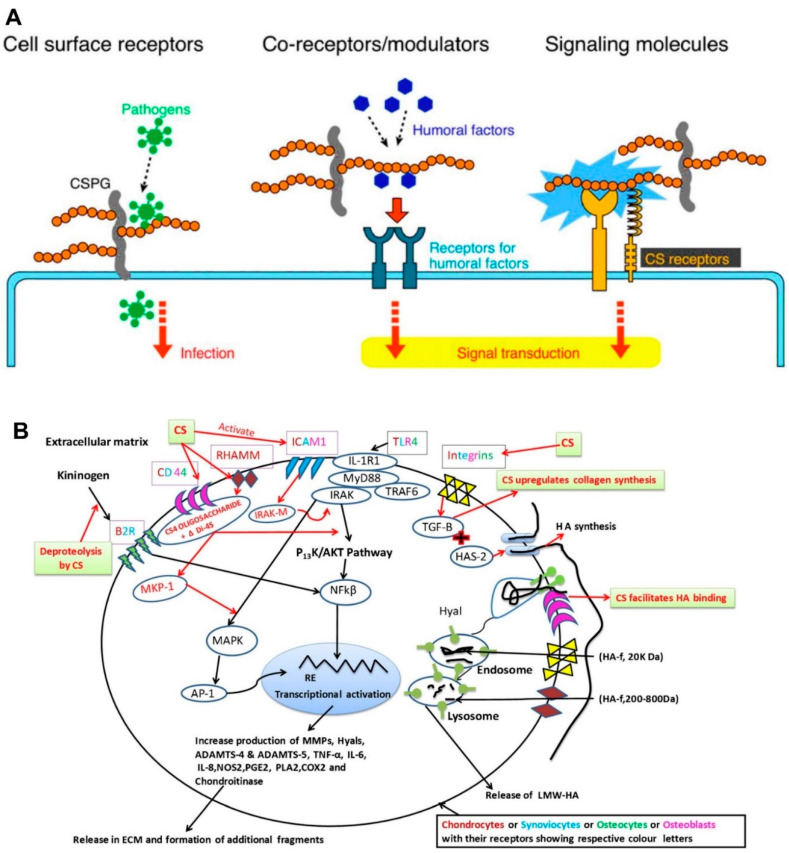
Figure 7.
Mechanisms of action regarding CS. (A) Receptor or signal modulation of CS chains [1]. (copyright © 2023, Elsevier). (B) Anti-inflammatory activity of CS chains. The anti-inflammatory activity of CS with specific inflammatory pathways in different types of cells of osteoarthritis [3]. (copyright © 2023, Springer Science+ Business Media New York). Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation primary response gene88 (MyD88), interleukin receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF-6), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), MAPK-phosphatase 1 (MKP-1), response element, specific sequences of DNA (RE), activator protein-1 (AP-1), HA synthase-2 (HAS2), Hyaluronidase (Hyal), aggrecanases (ADAMTS), cyclooxygenase2 (COX-2), interleukin-1 (IL-1), phospholipase A2 (LPA2), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), monosulfated disaccharides of CS, sulfated in position 4 (ΔDi-4S).