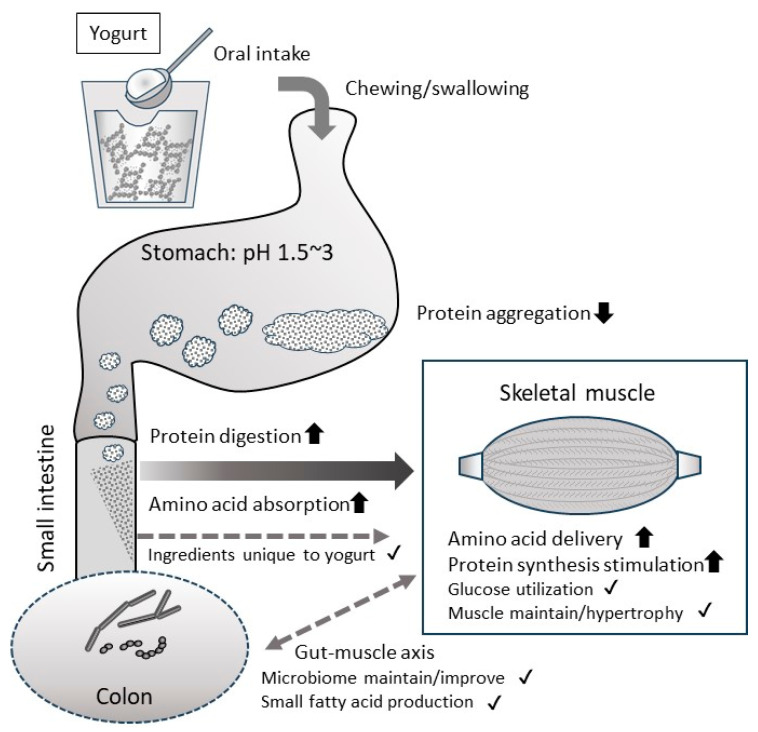
Figure 2.
Expected health benefits of consuming milk protein as yogurt on skeletal muscle. The milk proteins in yogurt are soft, acidified gel, so they will not aggregate tightly in the stomach. This will facilitate mixing with gastric juice through gastric peristalsis, pre-digestion with pepsin, and transport to the small intestine. Milk proteins that reach the small intestine are neutralized and then rapidly digested by pancreatin. Therefore, overall, milk protein intake as yogurt can be expected to improve the digestibility/absorption of proteins. However, care must be taken as it largely depends on the physical properties of the yogurt. Because milk protein in yogurt is highly digestible and absorbable, it is expected that the supply of amino acids to skeletal muscles will improve, leading to increased skeletal muscle protein synthesis. The unique ingredients and bacterial body contained in yogurt can have a positive effect on skeletal muscles via the gut–muscle axis and so on. By accumulating these positive effects, we can expect to maintain and increase skeletal muscle mass over the long term. However, most of these benefits have not yet been definitively proven and require further research. The arrows in the figure indicate benefits for which some evidence has been shown. The checkmarks in the figure indicate benefits that can be expected based on previous knowledge, although there is no direct evidence.