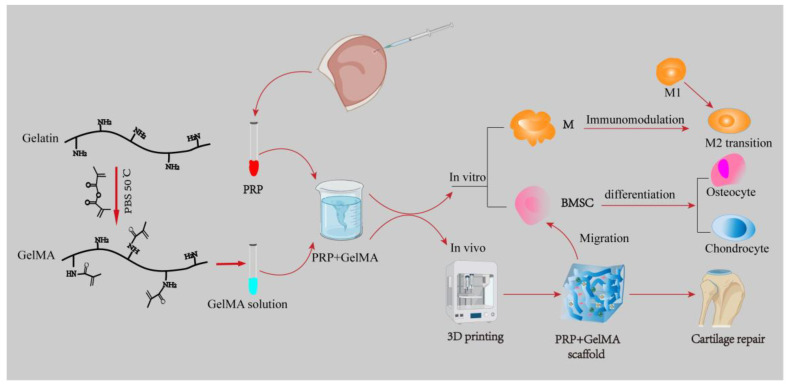
Figure 3.
PRP was extracted from whole blood collected in the ear vein of rabbits, gelatin was photo-modified into GelMA, and then the two were mixed to form a PRP–GelMA composite biomimetic hydrogel scaffold. In vivo, it can be used as an implant material by itself to repair cartilage tissue. In vitro, the PRP–GelMA composite biomimetic hydrogel scaffold is involved in macrophage immunomodulation to promote cartilage repair, which not only inhibits macrophage transformation to M1 but also promotes macrophage transformation to M2, and at the same time, it also serves as a bridge to connect with the BMSC, which can migrate to the BMSC to help the cellular differentiation and promotes the formation of osteoblasts and chondrocytes. PRP: platelet-rich plasma; GelMA: gelatin methacrylate; M: macrophage; M1: macrophage1; M2: macrophage2; BMSC: bone marrow stem cell.