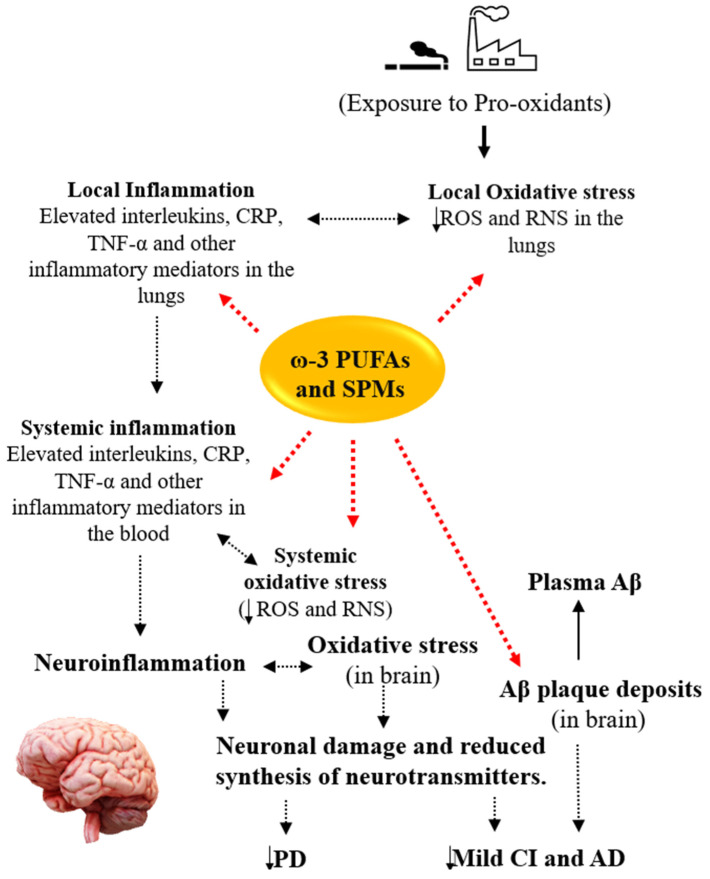
Figure 2.
Summary of the potentials of ω-3 PUFAs in managing COPD comorbid with CI. ω-3 PUFAs inhibit inflammatory pathways, activate antioxidant enzymes, improve Aβ clearance from the brain, and block inflammatory mediators from entering the brain. Aβ: amyloid-beta; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CI: cognitive impairment; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRP: C-reactive protein; PD: Parkinson’s disease; ω-3 PUFAs: omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; RNS: reactive nitrogen species; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SPMs: specialised pro-resolvin mediators; TNF-α: tumour necrosis factor-alpha.