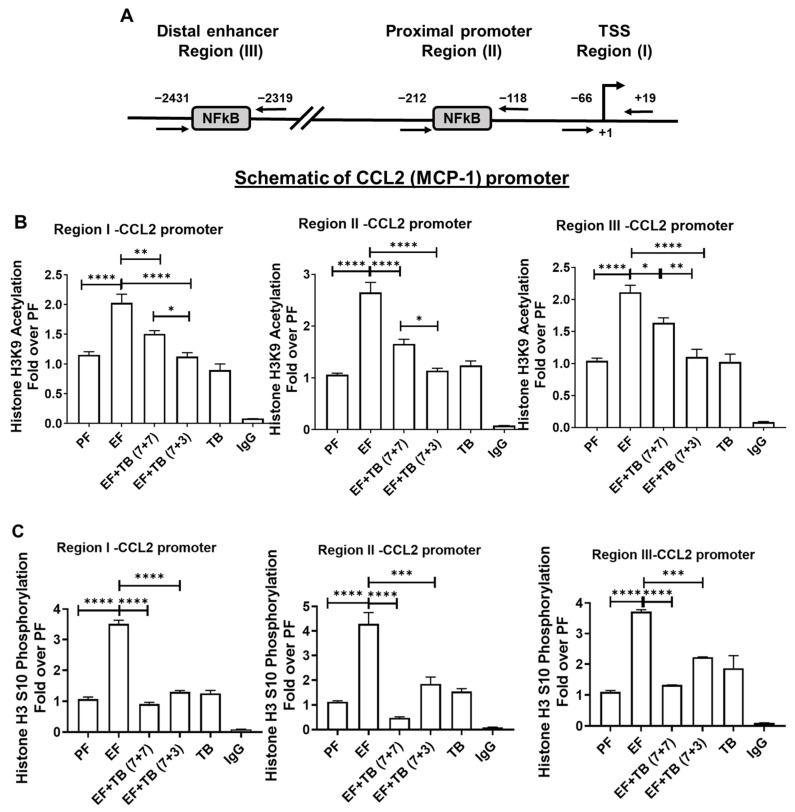
Figure 3.
Effect of tributyrin administration on chronic ethanol-induced promoter-associated histone H3 modifications at CCL2 promoter in the liver: Mice were fed either a control diet (pair-fed, PF) or ethanol (ethanol-fed; EF) (5% v/v)-containing diet. Tributyrin (TB; 2 g/kg) was orally administered to ethanol-fed mice as a preventive (EF + TB (7 + 7)) or interventional (EF + TB (7 + 3)) treatment strategy. (A) Schematic of CCL2 promoter: Locations of transcription factor NFκB binding sites and ChIP-PCR primer pairs for analysis of epigenetic modifications are denoted as regions I–III. The coordinate locations shown are with respect to the transcription start site in REFSEQ NM_011333. Hepatic CCL2 promoter-associated histone modifications were assessed by analyzing chromatin that was immunoprecipitated with (B) acetylated anti–histone H3 lysine9 (H3K9) and (C) phosphorylated anti-histone H3 serine 10 (H3S10) antibodies. Levels of histone modifications were measured using primers specific for regions I, II, and III, as shown in the schematic. Differences are expressed as fold-over PF after normalizing for input DNA. Statistical analysis: mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 compared with PF or EF via ANOVA with Bonferroni’s test (n = 5–8).