Figure 12.
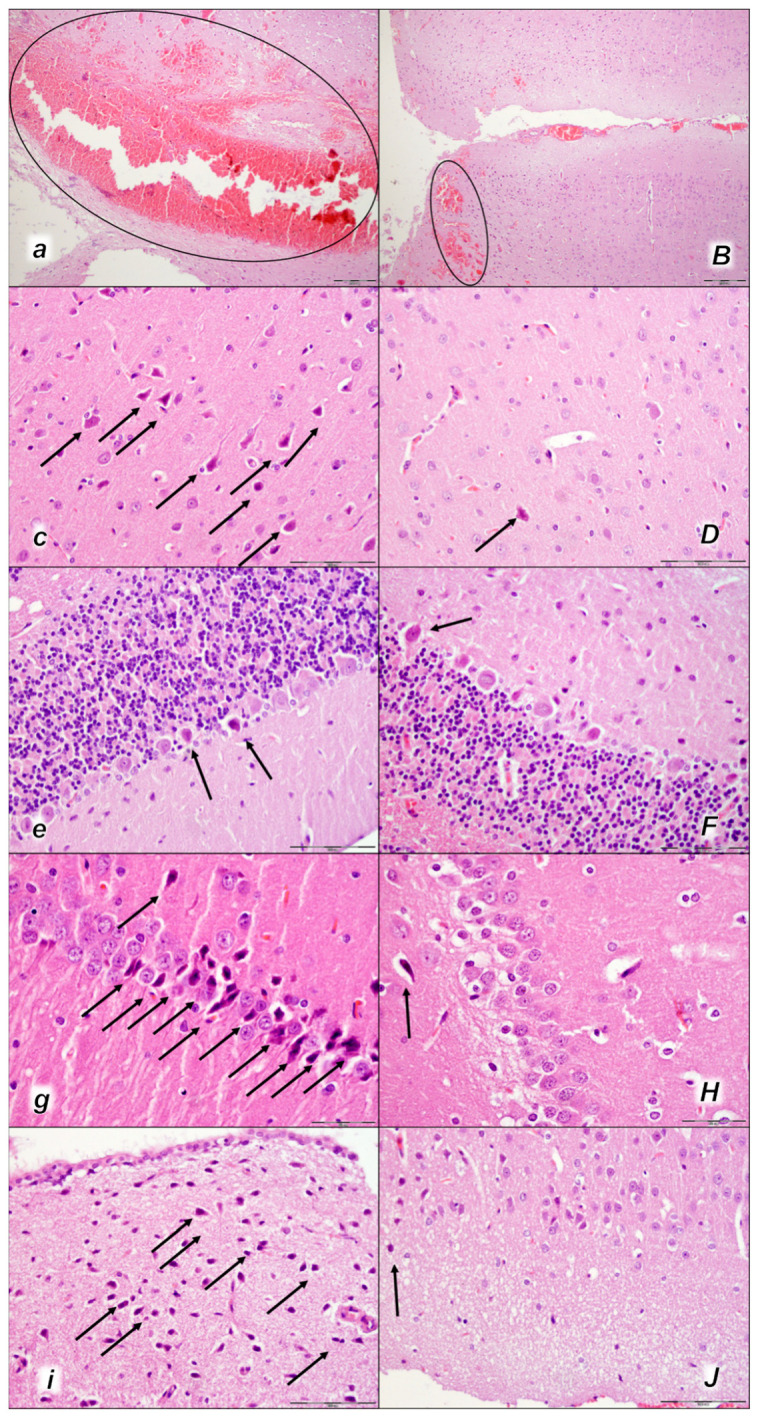
Brain neuropathological changes 30 min following laurate application into the inferior caval vein (a–J). In the control rats (italic small letters), a pronounced edema and congestion in the brain tissue were observed. Focal, pronounced, and deep intracerebral hemorrhage involving areas of brain tissue was observed, affecting areas of the neocortex, the corpus callosum, the amygdala, and the striatum in the brain tissue (a) (marked area). Moderate and severe neurodegenerative changes of the central nervous system, such as rare karyopyknotic cells affecting the cerebral (c) and cerebellar (e) cortex, a karyopyknosis and degeneration of the Purkinje cells of the cerebellar cortex, and karyopyknosis of cortical neurons, were observed (black arrows), as well as karyopyknosis of cortical neurons, hypothalamic neurons (g), and pyramidal cells of the hippocampus (i) (black arrows). In the BPC 157-treated rats (capital italic letters), only mild edema and congestion in the brain tissue were observed. Intracerebral hemorrhage was visible only within superficial layers of the neocortex (marked area) (B). BPC 157-treated rats presented no or only rare karyopyknotic cells in all four regions: the cerebrum (D), cerebellum (F), hypothalamus/thalamus (H), and hippocampus (J). (HE staining; magnification 100×; scale bar 200 µm (a,B); magnification 400×; scale bar 100 µm (c–J)).
