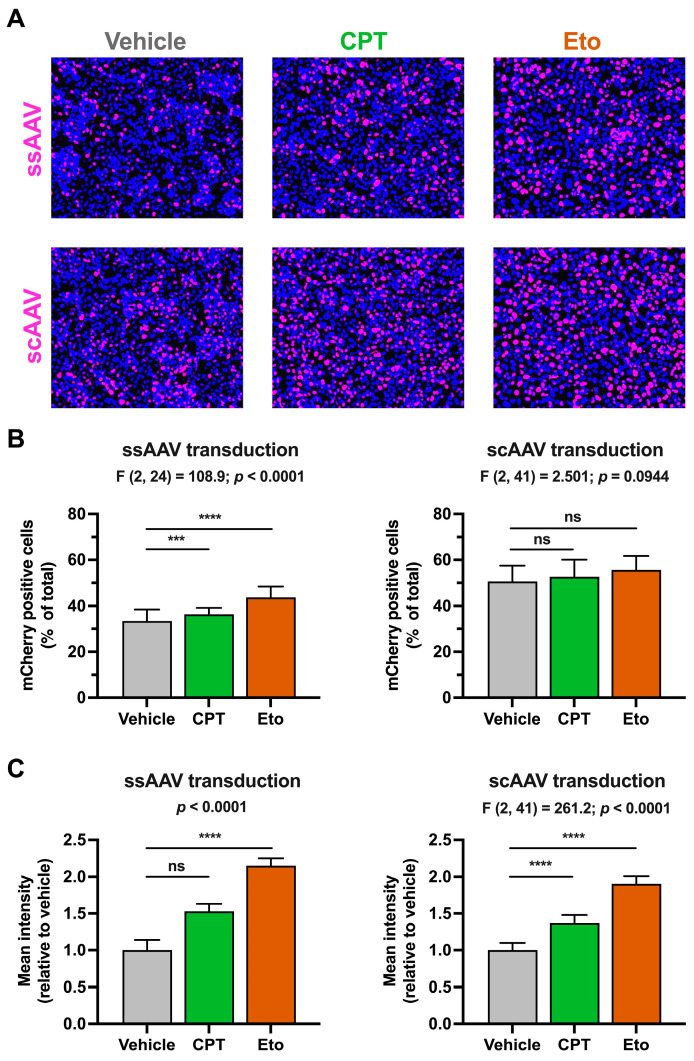
Figure 2.
Camptothecin and etoposide increase rAAV transduction. Cells were treated for one hour with either vehicle, 2.5 μM of CPT or 50 μM of Eto, and then transduced with ssAAV (2500 vg/cell) or scAAV (100 vg/cell). mCherry accumulation was measured 4 days after. (A) Representative overlay images of the mCherry accumulation (magenta) and nuclei staining (blue) in ssAAV- (upper panels) and scAAV- (lower panels) transduced cells. (B) Quantitation of the percentage of mCherry-positive cells relative to the total number of cells in each experimental condition. Results from ssAAV-transduced cells are shown on the left graph, while results from scAAV-transduced cells are on the right graph. (C) Quantitation of the mCherry mean fluorescence intensity signal in each condition relative to vehicle-treated condition that was set as 1. Results from ssAAV-transduced cells are shown on the left graph, while results from scAAV-transduced cells are on the right graph. Data displayed in graphs are the mean values and standard deviation of three (in ssAAV) or five (in scAAV) independent experiments performed in triplicates (n = 9 or n = 15). Data from (B,C) (only right graph) that were normally distributed were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Instead, data shown in the left graph in panel C were not normally distributed and therefore, they were analyzed using nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Statistical information is shown above each graph. Dunnett’s and Dunn’s tests were used to determine the statistical significance in pairwise comparisons (n.s.: not significant; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001).