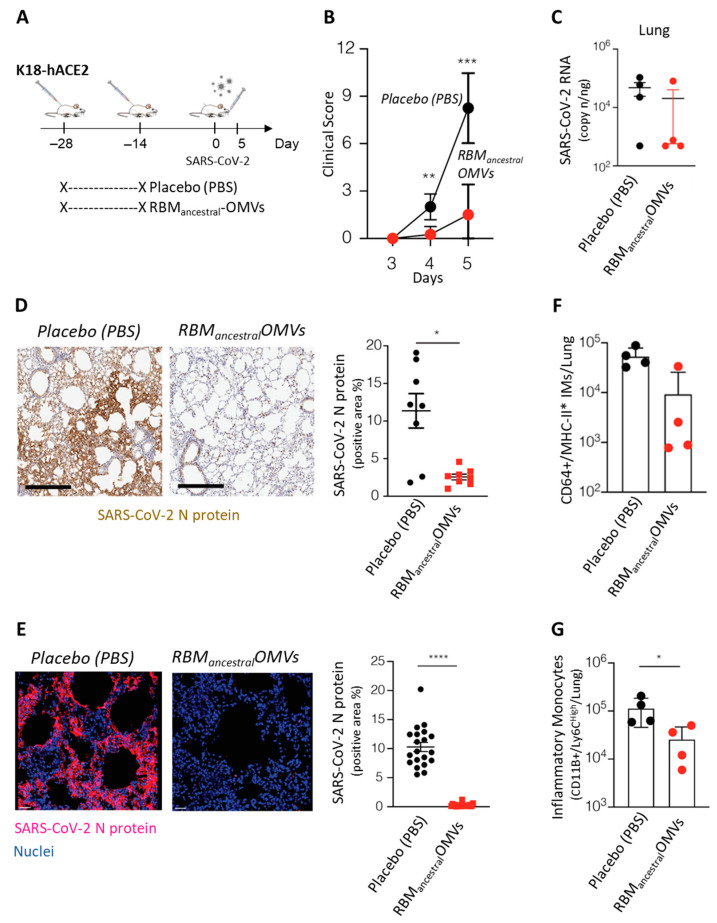
Figure 3.
Immunization with RBMancestral- OMVs protects against SARS-CoV-2 challenge in hACE2-transgenic mice. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental setup. K18-hACE2 mice (C57BL/6 background) received two intraperitoneal immunizations (at days −28 and −14) of 10 μg of OMVs vaccine (n = 4) or Placebo (PBS) (n = 4) prior to intranasal infection with 1 × 105 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2. Lung were collected and analysed five days after SARS-CoV-2 infection. (B) Mice were observed daily for clinical symptoms to assess severity of disease based on respiration, coat condition, posture, social behaviour, and palpebral aperture. (C) SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the lung was quantified by quantitative PCR with reverse transcription (RT–qPCR) 5 days after infection. (D) Representative immunohistochemical micrographs of lung sections 5 days post SARS-CoV-2 infection. N-SARS-CoV-2 expression is shown in brown. Scale bars, 300 μm. Right panel, quantification of N-SARS-CoV-2 signal, each dot represents a mouse. (E) Representative confocal immunofluorescence micrographs of lung sections from PBS-treated mice (left) or RBMancestral-OMVs immunized mice (right) 5 days post SARS-CoV-2 infection. N-SARS-CoV-2-positive cells are depicted in purple and nuclei in blue. Scale bar represents 30 μm. Right panel, quantification of N-SARS-CoV-2 signal, each dot represents a different stack. (F) Absolute numbers of CD11b+/Ly6Chigh inflammatory monocytes in the lung of the indicated mice 5 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection. (G) Absolute numbers of CD64+/MHC-II+ inflammatory monocytes in the lung of the indicated mice. * p value < 0.05, ** p value < 0.01, *** p value < 0.001, **** p value < 0.0001.