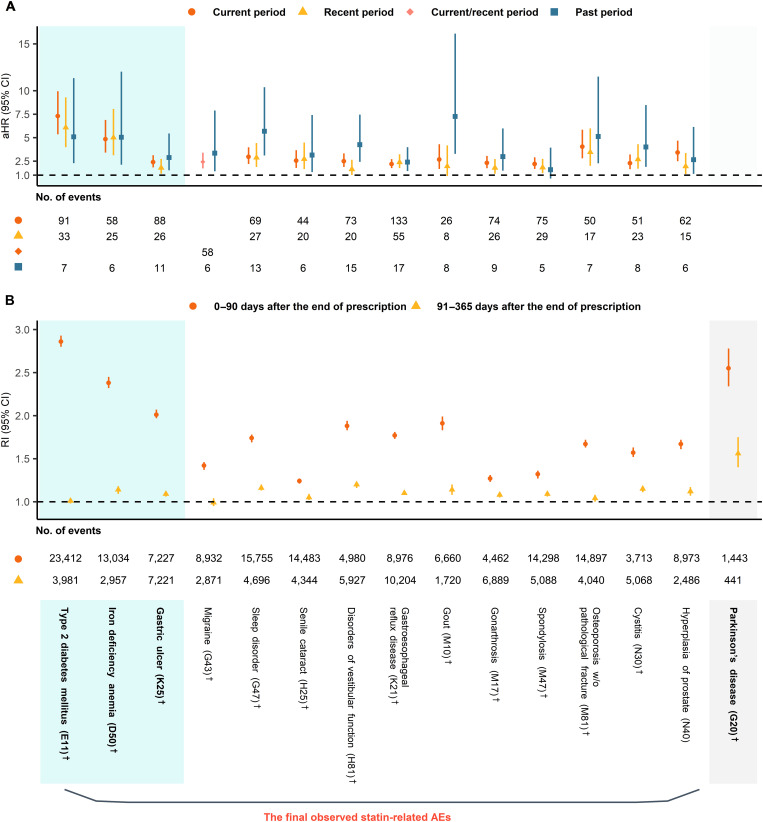
Fig. 2. Adjusted hazard ratios and relative incidences of candidate statin-related adverse effects.
All aHRs were adjusted for total cholesterol and residential area as a random effect. PD was excluded in (A) because of the insufficient sample size. (A) Results of time-dependent Cox regression for candidate statin-related AEs with aHRs and 95% CIs for each period. (B) Results of SCCS design for candidate statin-related AEs, and PD with RIs and 95% CIs for each period. We detected 14 statin-related AEs using (A) and (B). †Diagnoses matched on the previously known AE. AE, adverse effect; aHR, adjusted hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; PD, Parkinson's disease; RI, relative incidence; SCCS, self-controlled case series; w/o, without.