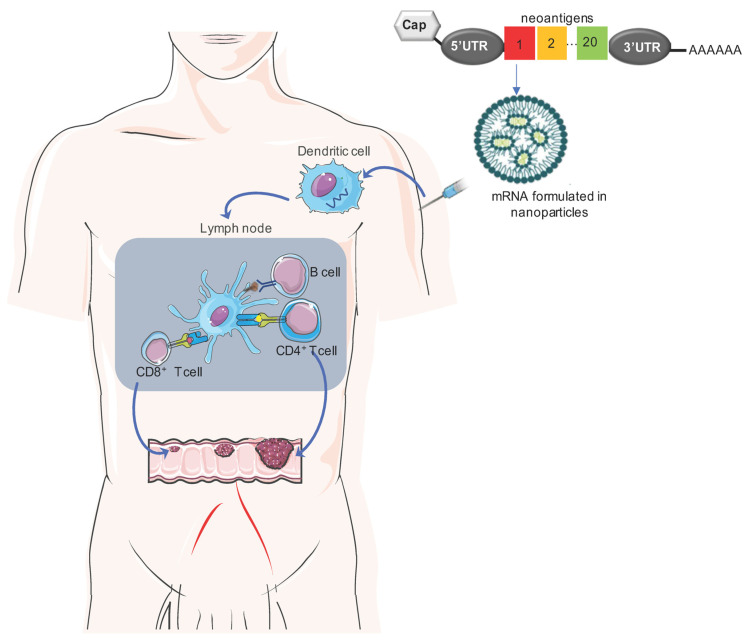
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the mechanism of action of mRNA cancer vaccines: An optimal mRNA vaccine should comprise a variety of neoantigens, including validated neoantigens, predicted neoantigens, and mutations in driver genes, which can collectively reduce the potential for tumor evasion. Upon delivery via nanoparticles, the mRNA vaccine actively targets and activates antigen-presenting cells, such as DCs, through interactions with TLR-7 or TLR-8. Subsequently, mature DCs migrate to lymph nodes, initiating robust B- and T-cell immune responses.