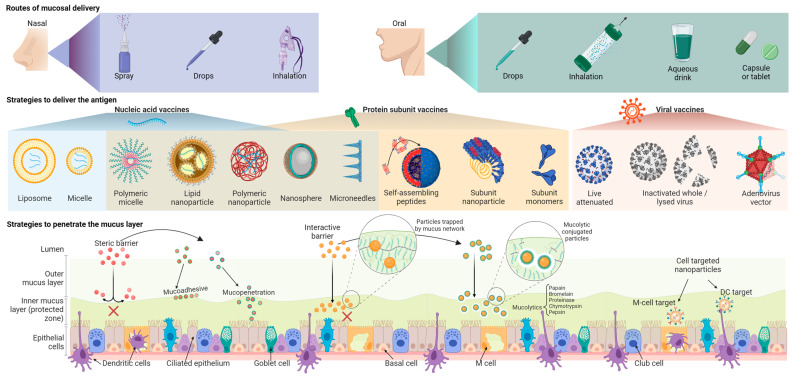
Figure 3.
Strategies to improve the delivery, penetration, uptake, and immunogenicity of respiratory mucosal vaccines. Vaccines targeting the respiratory mucosa can be delivered nasally (drops, spray, or inhalation) or orally (drops, oral inhalation, aqueous drink, or capsule/tablet). The target antigens can be delivered as nucleic acid or protein subunit vaccines packaged in different lipid/non-lipid nanoparticles or by traditional live-attenuated or inactivated whole virus vaccines. Post-COVID, the adenoviral vector system has gained interest as an intranasal/inhaled vaccine delivery platform. Facilitating antigen delivery by nanoparticles involves mucoadhesive, mucopenetrating, or mucolytic strategies. Created with BioRender.com.