Abstract
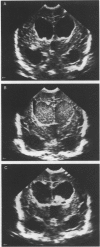
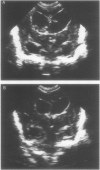
AIM: Phase I study to evaluate intraventricular fibrinolytic treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) as a method of clearing blood from the cerebrospinal fluid, and thus preventing permanent hydrocephalus. METHODS: Twenty two preterm infants, aged 7 to 26 days, with progressive posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation (ventricular width > 4 mm over 97th centile) received one to five intraventricular bolus injections of 1.0 mg or 0.5 mg tPA at intervals of one to seven days. RESULTS: The mean cerebrospinal fluid concentration of tPA 24 hours after 1 mg was 1860 micrograms/ml. The half life of tPA in cerebrospinal fluid was about 24 hours. Twenty one (95%) infants survived, 12 (55%) without shunt surgery. One infant had secondary intraventricular haemorrhage. CONCLUSION: Intraventricular tPA resulted in survival without a shunt for most of the infants, but with some risk. Failure may have been due to plasminogen deficiency, an inhibitor, or late intervention.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew M., Brooker L., Leaker M., Paes B., Weitz J. Fibrin clot lysis by thrombolytic agents is impaired in newborns due to a low plasminogen concentration. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Sep 7;68(3):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar M., Kadam S., Hiatt I. M., Hegyi T. Serial lumbar punctures in prevention of post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):446–450. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinker T., Seifert V., Dietz H. Subacute hydrocephalus after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: its prevention by intrathecal fibrinolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Neurosurgery. 1992 Aug;31(2):306–312. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199208000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. M., Grace M. G., Weir B. K. Treatment of intraventricular hemorrhage with tissue plasminogen activator. Neurosurgery. 1993 Jun;32(6):941–947. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199306000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. M., Weir B. K., Kassell N. F., Disney L. B., Grace M. G. Intracisternal recombinant tissue plasminogen activator after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1991 Aug;75(2):181–188. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Shackelford G. D., Volpe J. J. A potential mechanism of pathogenesis for early posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in the premature newborn. Pediatrics. 1984 Jan;73(1):19–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgins R. J., Boydston W. R., Hudgins P. A., Adler S. R. Treatment of intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant with urokinase. A preliminary report. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1994;20(3):190–197. doi: 10.1159/000120786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larroche J. C. Post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus in infancy. Anatomical study. Biol Neonate. 1972;20(3):287–299. doi: 10.1159/000240472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I. Measurement of the growth of the lateral ventricles in preterm infants with real-time ultrasound. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Dec;56(12):900–904. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.12.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liptak G. S., Gellerstedt M. E., Klionsky N. Isosorbide in the medical management of hydrocephalus in children with myelodysplasia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1992 Feb;34(2):150–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1992.tb14981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani J. F., Pasternak J. F., Mathew O. P., Allan W. C., Mills M. T., Casper J., Volpe J. J. Failure of daily lumbar punctures to prevent the development of hydrocephalus following intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):278–281. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80495-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Sherry S. Thrombolytic therapy: current status (1). N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1512–1520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfrank L., Lippitz B., Groth M., Bertalanffy H., Gilsbach J. M. Effect of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on clot lysis and ventricular dilatation in the treatment of severe intraventricular haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1993;122(1-2):32–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01446983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoi K., Yoshimoto T., Takahashi A., Fujiwara S., Koshu K., Sugawara T. Prospective study on the prevention of cerebral vasospasm by intrathecal fibrinolytic therapy with tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Neurosurg. 1993 Mar;78(3):430–437. doi: 10.3171/jns.1993.78.3.0430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D., Sclabassi R. J., Horton J. A. Lysis of intraventricular blood clot with urokinase in a canine model: Part 3. Effects of intraventricular urokinase on clot lysis and posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 1986 Oct;19(4):553–572. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198610000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde V., Schaller C., Hassler W. E. Intraventricular recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for lysis of intraventricular haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Apr;58(4):447–451. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART G. T. FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY IN MENINGITIS AND VENTRICULITIS. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:355–359. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolke D., Seifert V. Single intracisternal bolus of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: preliminary assessment of efficacy and safety in an open clinical study. Neurosurgery. 1992 Jun;30(6):877–881. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199206000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Keohane M. E., VanderBerg S. R., Gonias S. L. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the cerebrospinal fluid as an index of neurological disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994 Apr;5(2):167–171. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199404000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw A., Creighton L., Gaffney P. Fibrinolysis in cerebrospinal fluid after intraventricular haemorrhage. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jul;66(7 Spec No):808–809. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.7_spec_no.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw A. Endogenous fibrinolysis in neonatal cerebrospinal fluid. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Nov;152(11):928–930. doi: 10.1007/BF01957533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw A., Mowinckel M. C., Abildgaard U. Low levels of plasminogen in cerebrospinal fluid after intraventricular haemorrhage: a limiting factor for clot lysis? Acta Paediatr. 1995 Aug;84(8):933–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw A., Mowinckel M. C., Fellman V., Abildgaard U. Endogenous tissue plasminogen activator in neonatal cerebrospinal fluid. Eur J Pediatr. 1996 Feb;155(2):117–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02075763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw A., Rivers R. P., Creighton L., Gaffney P. Low dose intraventricular fibrinolytic treatment to prevent posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Jan;67(1 Spec No):12–14. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.1_spec_no.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabramski J. M., Spetzler R. F., Lee K. S., Papadopoulos S. M., Bovill E., Zimmerman R. S., Bederson J. B. Phase I trial of tissue plasminogen activator for the prevention of vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1991 Aug;75(2):189–196. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]