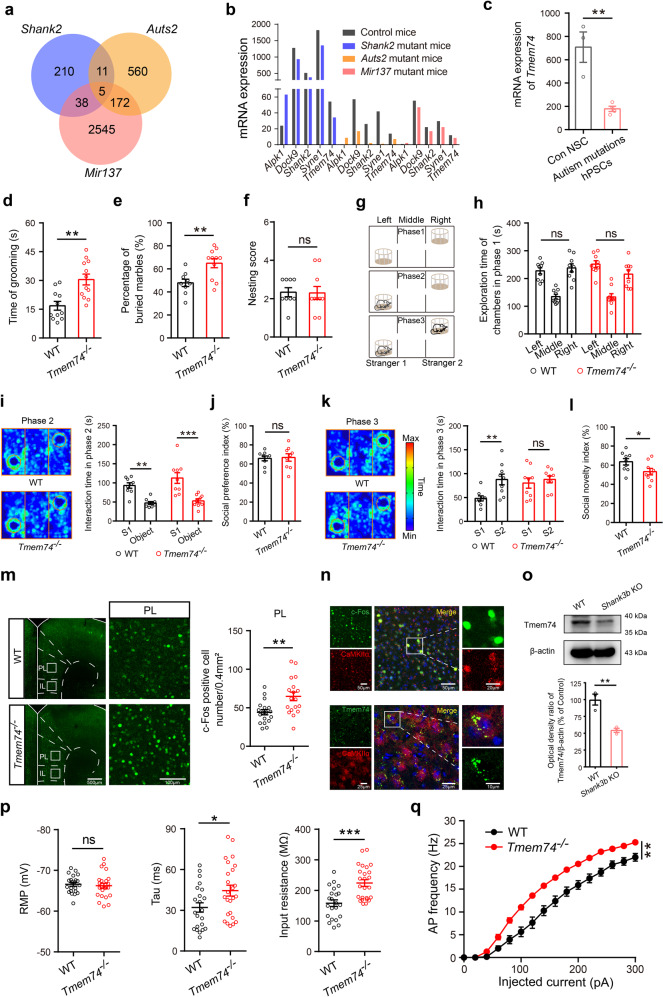
Fig. 1. Tmem74−/− mice display autistic-like behaviors and exhibit abnormal electrophysiological properties in PL pyramidal neurons.
a An overlapping Venn diagram of transcriptomic differential genes in three types of mice with autistic-like behaviors. b The mRNA expression of 5 overlapping differentially expressed genes. c The mRNA expression of Tmem74 in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). d Quantification of the time in self-grooming during the 10-min free movement (n = 11 WT mice, n = 12 Tmem74−/− mice). e The percentage of buried marbles (n = 9 WT mice, n = 11 Tmem74−/− mice). f The nesting ability (n = 9 WT mice, n = 10 Tmem74−/− mice). g Schematic of the three-chamber social test. h The mice preference for either the left or right chamber during phase 1 (n = 9 WT mice, n = 9 Tmem74−/− mice). i Left: Representative heatmaps of trajectory in phase 2 of three-chamber tests. Right: The time of interacting with the S1 mouse and the empty object (n = 9 WT mice, n = 9 Tmem74−/− mice); S1: Strange mouse 1. j The social interaction preference index (n = 9 WT mice, n = 9 Tmem74−/− mice). k Left: Representative heatmaps of trajectory in phase 3 of three-chamber tests. Right: The interaction time with S2 and S1 mouse (n = 9 WT mice, n = 9 Tmem74−/− mice); S2: Strange mouse 2. l The social novelty index (n = 9 WT mice, n = 9 Tmem74−/− mice). m Left: Representative confocal images of the c-Fos (green) after social interaction in the subregion of mPFC (PL). Right: Quantitative results of c-Fos activation in PL (n = 3 in each group, and six views of slices were provided for each mouse). n Top: Representative images of immunofluorescence showed that c-Fos co-localized at the CaMKIIα-positive neurons in PL. Bottom: Representative images of co-localization of TMEM74 and CaMKIIα. o The protein level of TMEM74 in PL of Shank3b knockout mice (n = 3 in each group). p Quantification of RMP (Left), Tau (Middle), and Rin (Right) of membrane properties in PL pyramidal neurons under whole-cell recording (n = 22 cells from 7 WT mice, n = 25 cells from 5 Tmem74−/− mice). q Quantification of the AP frequency by current injections from 0 to 300 pA (stepped by 20 pA) (n = 22 cells from 7 WT mice, n = 25 cells from 5 Tmem74−/− mice). Data were presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns not significant. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test for c–f, j, l, m, o and p; Two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s post hoc test for h, i and k; Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test for q. mPFC medial prefrontal cortex, PL prelimbic cortex, RMP resting membrane potential, Tau time constant, Rin input resistant.