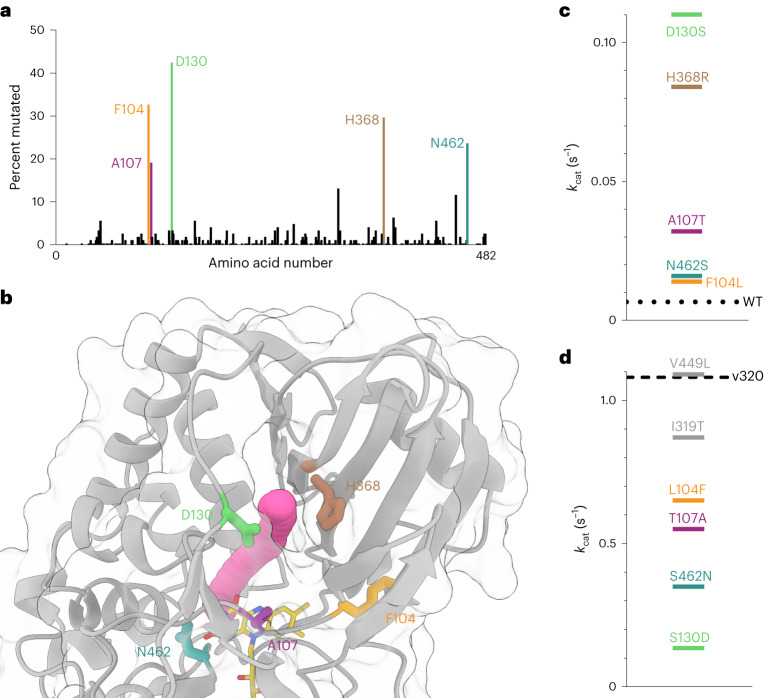
Fig. 2. Mutations near FAD are critical for a gain in oxygen reactivity.
a, One hundred and thirty-three variant sequences were isolated from our selection. The observed percentage of missense mutations at each amino acid location along the protein’s sequence is plotted. Note that these variant sequences are not independent because the iterative mutagenesis used to create new mutant libraries was done using a pool of higher-activity variants as a template and is therefore subject to a founder effect between different generations of the selection. The color scheme in a applies to the rest of the figure. b, The crystal structure of wild-type NicA2 (Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID 5TTJ) is displayed with a tunnel diameter of ~1.4 Å identified by CAVER simulation rendered in magenta43. c, kcat values determined for single mutations in the background of wild-type NicA2. The dotted line indicates the kcat value of wild-type NicA2. d, kcat values determined for variants where mutations were removed from the background of NicA2 v320; each line represents the kcat value corresponding to single mutations back toward the wild-type NicA2. Note the tenfold difference in scale from the plot shown in c. The dashed line indicates the kcat value of NicA2 v320. The location of the amino acid positions L449 and T319 in the crystal structure can be seen in Extended Data Fig. 4.