Fig. 1 |. Proportion of familial and sporadic ALS cases attributed to mutations in the corresponding disease-causing genes.
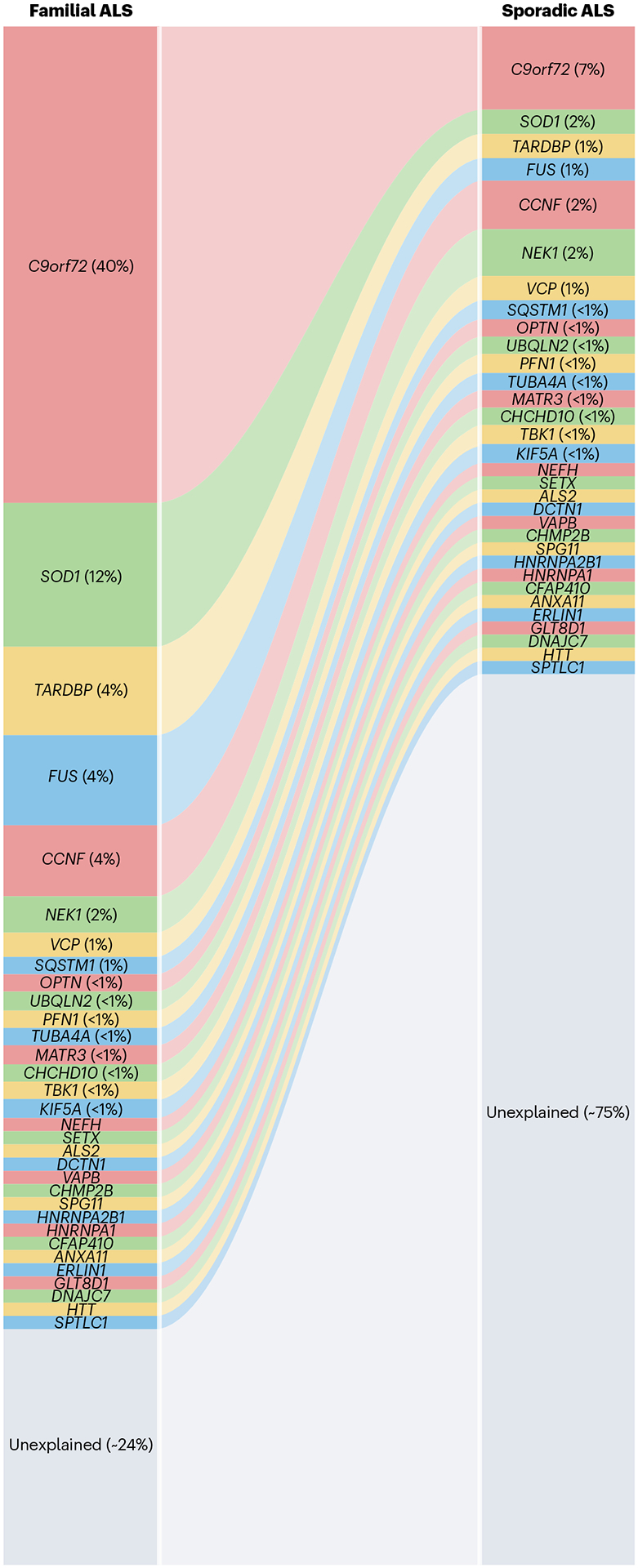
Mutations in the known amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) genes explain approximately 76% of familial and 25% of sporadic ALS231. The four most common ALS-associated genes, C9orf72, SOD1, TARDBP and FUS comprise 60% of familial and 11% of sporadic ALS. The proportion attributed to recently identified or rarely implicated genes has not been established.
